Emerging roles and context of circular RNAs
- PMID: 27612318
- PMCID: PMC5315638
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1386
Emerging roles and context of circular RNAs
Abstract
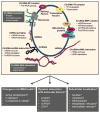
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) represent a large class of noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) that have recently emerged as regulators of gene expression. They have been shown to suppress microRNAs, thereby increasing the translation and stability of the targets of such microRNAs. In this review, we discuss the emerging functions of circRNAs, including RNA transcription, splicing, turnover, and translation. We also discuss other possible facets of circRNAs that can influence their function depending on the cell context, such as circRNA abundance, subcellular localization, interacting partners (RNA, DNA, and proteins), dynamic changes in interactions following stimulation, and potential circRNA translation. The ensuing changes in gene expression patterns elicited by circRNAs are proposed to drive key cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, that govern health and disease. WIREs RNA 2017, 8:e1386. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1386 For further resources related to this article, please visit the WIREs website.
Published 2016. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979;280:339–340. - PubMed
-
- Nigro JM, Cho KR, Fearon ER, Kern SE, Ruppert JM, Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Scrambled Exons. Cell. 1991;64:607–613. - PubMed
-
- Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss R, et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell. 2015;58:870–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

