Thyrotropin and CD40L Stimulate Interleukin-12 Expression in Fibrocytes: Implications for Pathogenesis of Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy
- PMID: 27612658
- PMCID: PMC5175425
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2016.0243
Thyrotropin and CD40L Stimulate Interleukin-12 Expression in Fibrocytes: Implications for Pathogenesis of Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy
Abstract
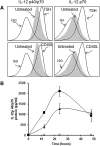
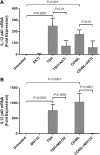
Background: Increased numbers of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells, known as fibrocytes, populate the peripheral circulation, orbit, and thyroid of patients with Graves' disease (GD). These cells have been implicated in the development of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. They can differentiate into myofibroblasts or adipocytes, produce inflammatory cytokines, and remodel tissue. This study sought to determine whether thyrotropin (TSH) and CD40 ligand (CD40L), implicated in the pathogenesis of GD, induce interleukin-12 (IL-12) in human fibrocytes.
Materials and methods: IL-12 protein concentrations and mRNA levels were measured by Luminex and real-time polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Flow cytometry assessed intracellular IL-12 concentrations. Vector containing IL-12p40 promoter was transfected into cultured fibrocytes, and promoter activity was monitored using luciferase assay.
Results: TSH and CD40L stimulated intracellular IL-12 protein accumulation in peripheral blood fibrocytes. Inhibiting Akt and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity diminished IL-12 expression in fibrocytes, while TSH did not induce promoter activity. TSH-mediated IL-12 production required de novo synthesized proteins and augmented IL-12 mRNA stability. IL-12 production mediated by CD40L required tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6.
Conclusion: TSH and CD40L induce IL-12 expression in fibrocytes, and Akt and NF-κB mediate this activity. Given the importance of IL-12 in immune function, its production by fibrocytes may promote an inflammatory immune response and tissue remodeling in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.
Keywords: Graves' disease; autoimmunity; fibrocyte; interleukin-12; thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Disclosure Statement The authors have no proprietary or commercial interest in any material discussed in this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 production in CD40-engaged fibrocytes in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: involvement of Akt and NF-κB.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Nov 21;53(12):7746-53. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9861. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 23092922 Free PMC article.
-
Thyrotropin receptor and CD40 mediate interleukin-8 expression in fibrocytes: implications for thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;112:26-37. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25411513 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT pathway mediates induction of IL-1RA by TSH in fibrocytes: modulation by PTEN.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Sep;99(9):3363-72. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-1257. Epub 2014 May 19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24840811 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives on the role of orbital fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of Graves' ophthalmopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2016 Jan;142:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.02.007. Exp Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26675405 Review.
-
TSH-receptor-expressing fibrocytes and thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015 Mar;11(3):171-81. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.226. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25560705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential profiling of lacrimal cytokines in patients suffering from thyroid-associated orbitopathy.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 17;8(1):10792. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29113-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30018377 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Roles of CD34+ Fibrocytes Masquerading as Orbital Fibroblasts in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Feb 1;104(2):581-594. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-01493. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30445529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the CD40 rs1883832 polymorphism and Graves' disease risk: a meta-analysis.EXCLI J. 2019 Jan 23;18:10-20. eCollection 2019. EXCLI J. 2019. PMID: 30956635 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor-kappa B in Thyroid Autoimmunity and Cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 21;9:471. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00471. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30186235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy: Emergence of teprotumumab as a promising medical therapy.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan;34(1):101383. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2020.101383. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32088116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartalena L, Fatourechi V. 2014. Extrathyroidal manifestations of Graves' disease: a 2014 update. J Endocrinol Invest 37:691–700 - PubMed
-
- Smith TJ, Padovani-Claudio DA, Lu Y, Raychaudhuri N, Fernando R, Atkins S, Gillespie EF, Gianoukakis AG, Miller BS, Gauger PG, Doherty GM, Douglas RS. 2011. Fibroblasts expressing the thyrotropin receptor overarch thyroid and orbit in Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:3827–3837 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellini A, Mattoli S. 2007. The role of the fibrocyte, a bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor, in reactive and reparative fibroses. Lab Invest 87:858–870 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

