Expression of type III interferons (IFNλs) and their receptor in Sjögren's syndrome
- PMID: 27613139
- PMCID: PMC5108072
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12865
Expression of type III interferons (IFNλs) and their receptor in Sjögren's syndrome
Abstract
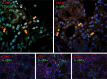
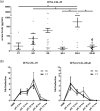
Type III interferons (IFNs) or IFN-λs (IFN-λ1/IL29, IFN-λ2/interleukin (IL)-28A and IFN-λ3/IL-28B) consist of a recently identified group of IFNs, implicated initially in several human diseases, including cancer and autoimmunity. In this study, we sought to investigate the expression of type III IFNs and their common receptor IFN-λR1/IL-28Ra in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Type III IFN expression was examined in minor salivary gland tissues (MSG), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), sera and resting or Toll-like receptor (TLR)-stimulated salivary gland epithelial cells (SGEC) from SS patients and sicca-complaining controls. All type III IFN family members were detected in ductal and acinar epithelia of MSGs from both SS patients and sicca controls. IFN-λ2/IL-28A and IFN-λ3/IL-28B were also expressed in infiltrating mononuclear cells. In SS patients with intermediate MSG lesions, the epithelial expression of IFN-λ2/IL-28A was more intense compared to sicca controls (P < 0·05). The receptor IFN-λR1/IL-28Ra was detected in all types of cells except fibroblasts, and was exceptionally strong in plasmatocytoid dendritic cells, indicating that they are susceptible to type III IFN-mediated regulation. In the periphery, only IFN-λ1/IL-29 was detected in the sera and was elevated significantly in SS patients with intermediate MSG inflammatory lesions compared to sicca controls (P = 0·0053). None of the type III IFNs was expressed constitutively in resting SGECs; they were all induced readily by TLR-3 stimulation, suggesting that the in-situ epithelial expression can be attributed to local microenvironment. Type III IFNs are expressed in MSGs in a similar pattern to type I IFNs and their expression is probably subjected to micro-environmental regulation, suggesting that they are implicated in the inflammatory processes occurring in the affected exocrine glands.
Keywords: TLRs; autoimmunity; cytokines; inflammation.
© 2016 British Society for Immunology.
Figures


References
-
- Tzioufas AG, Kapsogeorgou EK, Moutsopoulos HM. Pathogenesis of Sjogren's syndrome: what we know and what we should learn. J Autoimmun 2012; 39:4–8. - PubMed
-
- Spachidou M, Kapsogeorgou E, Moutsopoulos H, Manoussakis M. Toll‐like receptor‐3 triggering of salivary gland epithelial cells (SGEC) causes detachment‐induced cell death (anoikia) that is more pronounced in cells derived from Sjögren's syndrome patients. Ann of Rheum Dis 2007; 66: A36.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

