Microbleeds on MRI are associated with microinfarcts on autopsy in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
- PMID: 27613583
- PMCID: PMC5075970
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003184
Microbleeds on MRI are associated with microinfarcts on autopsy in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Abstract
Objectives: To identify in vivo MRI markers that might correlate with cerebral microinfarcts (CMIs) on autopsy in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA).
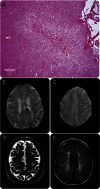
Methods: We included patients with neuropathologic evidence of CAA on autopsy and available antemortem brain MRI. Clinical characteristics and in vivo MRI markers of CAA-related small vessel disease were recorded, including white matter hyperintensities, cerebral microbleeds, cortical superficial siderosis, and centrum semiovale perivascular spaces. In addition, the presence of intracerebral hemorrhage on MRI was assessed. Evaluation of the presence and number of CMIs was performed in 9 standard histology sections.
Results: Of 49 analyzed patients with CAA, CMIs were present in 36.7%. The presence of ≥1 CMIs on autopsy was associated with higher numbers of microbleeds on antemortem MRI (median 8 [interquartile range 2.5-33.0] vs 1 [interquartile range 0-3], p = 0.003) and with the presence of intracerebral hemorrhage (44.4% vs 16.1%, p = 0.03). No associations between CMIs and other in vivo MRI markers of CAA were found. In a multivariable model adjusted for severe CAA pathology, higher numbers of microbleeds were independent predictors of the presence of CMIs on pathology.
Conclusions: CMIs are a common finding at autopsy in patients with CAA. The strong association between MRI-observed microbleeds and CMIs at autopsy may suggest a shared underlying pathophysiologic mechanism between these lesions.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Charidimou A, Werring DJ. Cerebral microbleeds and cognition in cerebrovascular disease: an update. J Neurol Sci 2012;322:50–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
