To evaluate of the effect of adding licorice to the standard treatment regimen of Helicobacter pylori
- PMID: 27614124
- PMCID: PMC9427648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2016.07.015
To evaluate of the effect of adding licorice to the standard treatment regimen of Helicobacter pylori
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of licorice in H. pylori eradication in patients suffering from dyspepsia either with peptic ulcer disease (PUD) or non-ulcer dyspepsia (NUD) in comparison to the clarithromycin-based standard triple regimen.
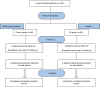
Methods: In this randomized controlled clinical trial, 120 patients who had positive rapid urease test were included and assigned to two treatment groups: control group that received a clarithromycin-based triple regimen, and study group that received licorice in addition to the clarithromycin-based regimen for two weeks. H. pylori eradication was assessed six weeks after therapy. Data was analyzed by chi-square and t-test with SPSS 16 software.
Results: Mean ages and SD were 38.8±10.9 and 40.1±10.4 for the study and control groups, respectively, statistically similar. Peptic ulcer was found in 30% of both groups. Response to treatment was 83.3% and 62.5% in the study and control groups, respectively. This difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion: Addition of licorice to the triple clarithromycin-based regimen increases H. pylori eradication, especially in the presence of peptic ulcer disease.
Keywords: Dyspepsia; Helicobacter pylori; Licorice; Peptic ulcer.
Copyright © 2016 Sociedade Brasileira de Infectologia. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hunt R.H., Xiao S.D., Megraud F., et al. Helicobacter pylori in developing countries. J Gastrointest Liver Dis. 2011;20:299–304. - PubMed
-
- Balakrishnan V., Pillai M.V., Raveendran P.M., Nair C.S. Deglycyrrhizinated liquorice in the treatment of chronic duodenal ulcer. J Assoc Physicians India. 1978;26:811–814. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins R.J., Girardi L.S., Turney E.A. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori eradication and reduced duodenal and gastric ulcer recurrence: a review. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:1244. - PubMed
-
- Laine L., Hopkins R.J., Girardi L.S. Has the impact of Helicobacter pylori therapy on ulcer recurrence in the United States been overstated? A meta-analysis of rigorously designed trials. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical