Nanocall: an open source basecaller for Oxford Nanopore sequencing data
- PMID: 27614348
- PMCID: PMC5408768
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw569
Nanocall: an open source basecaller for Oxford Nanopore sequencing data
Abstract
Motivation: The highly portable Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencer has enabled new applications of genome sequencing directly in the field. However, the MinION currently relies on a cloud computing platform, Metrichor (metrichor.com), for translating locally generated sequencing data into basecalls.
Results: To allow offline and private analysis of MinION data, we created Nanocall. Nanocall is the first freely available, open-source basecaller for Oxford Nanopore sequencing data and does not require an internet connection. Using R7.3 chemistry, on two E.coli and two human samples, with natural as well as PCR-amplified DNA, Nanocall reads have ∼68% identity, directly comparable to Metrichor '1D' data. Further, Nanocall is efficient, processing ∼2500 Kbp of sequence per core hour using the fastest settings, and fully parallelized. Using a 4 core desktop computer, Nanocall could basecall a MinION sequencing run in real time. Metrichor provides the ability to integrate the '1D' sequencing of template and complement strands of a single DNA molecule, and create a '2D' read. Nanocall does not currently integrate this technology, and addition of this capability will be an important future development. In summary, Nanocall is the first open-source, freely available, off-line basecaller for Oxford Nanopore sequencing data.
Availability and implementation: Nanocall is available at github.com/mateidavid/nanocall, released under the MIT license.
Contact: matei.david@oicr.on.caSupplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
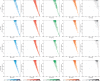
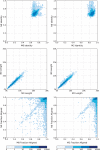
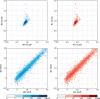

References
-
- Baum L.E. (1972) An equality and associated maximization technique in statistical estimation for probabilistic functions of Markov processes. Inequalities, 3, 1–8.
-
- Durbin R. et al. (1998) Biological Sequence Analysis: Probabilistic Models of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
-
- Ip C.L. et al. (2015) Minion analysis and reference consortium: phase 1 data release and analysis. F1000Research, 4, 10.12688/f1000research.7201.1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li H. (2013) Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv Preprint arXiv:1303.3997.
-
- Loman N.J. et al. (2015) A complete bacterial genome assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods, 12, 733–735. - PubMed

