Metabolic Markers to Predict Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Statin-Treated Patients (from the Treating to New Targets and the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels Trials)
- PMID: 27614854
- PMCID: PMC6686184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.07.054
Metabolic Markers to Predict Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Statin-Treated Patients (from the Treating to New Targets and the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels Trials)
Abstract
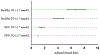
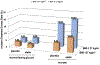
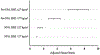
The goal of this analysis was to evaluate the ability of insulin resistance, identified by the presence of prediabetes mellitus (PreDM) combined with either an elevated triglyceride (TG >1.7 mmol/l) or body mass index (BMI ≥27.0 kg/m2), to identify increased risk of statin-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Consequently, a retrospective analysis of data from subjects without diabetes in the Treating to New Targets and the Stroke Prevention by Aggressive Reduction in Cholesterol Levels randomized controlled trials was performed, subdividing participants into 4 experimental groups: (1) normal fasting glucose (NFG) and TG ≤1.7 mmol/l (42%); (2) NFG and TG >1.7 mmol/l (22%); (3) PreDM and TG ≤1.7 mmol/l (20%); and (4) PreDM and TG >1.7 mmol/l (15%). Comparable groupings were created substituting BMI values (kg/m2 <27.0 and ≥27.0) for TG concentrations. Patients received atorvastatin or placebo for a median duration of 4.9 years. Incident T2DM, defined by developing at least 2 fasting plasma glucose (FPG) concentrations ≥126 mg/dl, an increase in FPG ≥37 mg/dl, or a clinical diagnosis of T2DM, was observed in 8.2% of the total population. T2DM event rates (statin or placebo) varied from a low of 2.8%/3.2% (NFG and TG ≤1.7 mmol/l) to a high of 22.8%/7.6% (PreDM and TG >1.7 mmol/l) with intermediate values for only an elevated TG >1.7 mmol/l (5.2%/4.3%) or only PreDM (12.8%/7.6%). Comparable differences were observed when BMI values were substituted for TG concentrations. In conclusion, these data suggest that (1) the diabetogenic impact of statin treatment is relatively modest in general; (2) the diabetogenic impact is accentuated relatively dramatically as FPG and TG concentrations and BMI increase; and (3) PreDM, TG concentrations, and BMI identify people at highest risk of statin-associated T2DM.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
Dr. Kohli is in the advisory board of Amgen and receives travel reimbursement from Pfizer, Inc. Dr. Waters receives remuneration for participating in clinical trial committees from Aastrom, Cerenis, CSL, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis; honoraria for lectures from Pfizer and Zydus Medica; and consulting fees from Novo Nordisk and Pfizer. Dr. Knowles receives Grants 5IRG222930034 from American Heart Association and is supported by a Clinical Scientist Development Award from the Doris Duke Charitable Trust. Other authors have no conflicts to report.
Figures
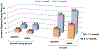
References
-
- Sattar N, Preiss D, Murray HM, Welsh P, Buckley BM, de Craen AJ, Seshasai SR, McMurray JJ, Freeman DJ, Jukema JW, Macfarlane PW, Packard CJ, Stott DJ, Westendorp RG, Shepherd J, Davis BR, Pressel SL, Marchioli R, Marfisi RM, Maggioni AP, Tavazzi L, Tognoni G, Kjekshus J, Pedersen TR, Cook TJ, Gotto AM, Clearfield MB, Downs JR, Nakamura H, Ohashi Y, Mizuno K, Ray KK, Ford I. Statins and risk of incident diabetes: a collaborative meta-analysis of randomised statin trials. Lancet 2010;375:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Preiss D, Seshasai SR, Welsh P, Murphy SA, Ho JE, Waters DD, DeMicco DA, Barter P, Cannon CP, Sabatine MS, Braunwald E, Kastelein JJ, de Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Pedersen TR, Tikkanen MJ, Sattar N, Ray KK. Risk of incident diabetes with intensive-dose compared with moderate-dose statin therapy: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2011;305:2556–2564. - PubMed
-
- Waters DD, Ho JE, DeMicco DA, Breazna A, Arsenault BJ, Wun CC, Kastelein JJ, Colhoun H, Barter P. Predictors of new-onset diabetes in patients treated with atorvastatin: results from 3 large randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:1535–1545. - PubMed
-
- Sattar N, Taskinen MR. Statins are diabetogenic—myth or reality? Atheroscler Suppl 2012;13:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Mihaylova B, Emberson J, Blackwell L, Keech A, Simes J, Barnes EH, Voysey M, Gray A, Collins R, Baigent C. The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with statin therapy in people at low risk of vascular disease: meta-analysis of individual data from 27 randomised trials. Lancet 2012;380:581–590. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

