Anti-inflammatory and antifatigue effect of Korean Red Ginseng in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 27616896
- PMCID: PMC5005313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.07.006
Anti-inflammatory and antifatigue effect of Korean Red Ginseng in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background: Korean Red Ginseng (KRG) is a well-known natural product with anticarcinogenic and antioxidant effects. We evaluated the antifatigue effect of KRG in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Methods: Eighty patients with NAFLD were prospectively randomized to receive 3 wk of KRG or placebo in addition to counseling on healthy eating and regular exercise. Liver function test, proinflammatory cytokines, adiponectin, antioxidant activity, and fatigue score were measured and compared according to the body mass index between the KRG and placebo groups.
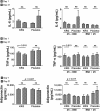
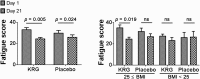
Results: The liver function tests were significantly improved after 3 wk of treatment in both groups. The mean levels (at baseline and after treatment) of tumor necrosis factor-α were 108.0 pg/mL ± 54.8 pg/mL and 92.7 pg/mL ± 39.0 pg/mL (p = 0.018) in the KRG group and 123.1 pg/mL ± 42.1 pg/mL and 127.5 pg/mL ± 62.2 pg/mL (p = 0.694) in the placebo group, respectively. There was a significant difference in change of adiponectin levels between the KRG (7,751.2 pg/mL ± 3,108.1 pg/mL and 8,197.3 pg/mL ± 2,714.5 pg/mL) and placebo groups (7,711.6 pg/mL ± 3,041.3 pg/mL and 7,286.1 pg/mL ± 5,188.7 pg/mL, p = 0.027). In patients with overweight, the fatigue score was significantly decreased in the KRG group (35.0 ± 13.2 and 24.5 ± 8.9, p = 0.019).
Conclusion: Our results show that KRG might be effective in reducing proinflammatory cytokine and fatigue in overweight patients with NAFLD, in addition to improvements in adiponectin levels.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; adiponectin; chronic hepatitis; fatty liver.
Figures



References
-
- Brunt E.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: what the pathologist can tell the clinician. Dig Dis. 2012;30:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Kleiner D.E., Brunt E.M., Van Natta M., Behling C., Contos M.J., Cummings O.W., Ferrell L.D., Liu Y.C., Torbenson M.S., Unalp-Arida A. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1321. - PubMed
-
- Review Team, LaBrecque D.R., Abbas Z., Anania F., Ferenci P., Khan A.G., Goh K.L., Hamid S.S., Isakov V., Lizarzabal M. World Gastroenterology Organisation global guidelines: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Newton J.L., Jones D.E., Henderson E., Kane L., Wilton K., Burt A.D., Day C.P. Fatigue in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is significant and associates with inactivity and excessive daytime sleepiness but not with liver disease severity or insulin resistance. Gut. 2008;57:807–813. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

