Wnt signaling in cancer
- PMID: 27617575
- PMCID: PMC5357762
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2016.304
Wnt signaling in cancer
Abstract
Wnt signaling is one of the key cascades regulating development and stemness, and has also been tightly associated with cancer. The role of Wnt signaling in carcinogenesis has most prominently been described for colorectal cancer, but aberrant Wnt signaling is observed in many more cancer entities. Here, we review current insights into novel components of Wnt pathways and describe their impact on cancer development. Furthermore, we highlight expanding functions of Wnt signaling for both solid and liquid tumors. We also describe current findings how Wnt signaling affects maintenance of cancer stem cells, metastasis and immune control. Finally, we provide an overview of current strategies to antagonize Wnt signaling in cancer and challenges that are associated with such approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

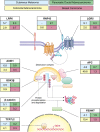
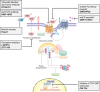
References
-
- Sharma R. Wingless, a new mutant in D. melanogaster. Drosoph Inf Serv 1973; 50: 134.
-
- Nüsslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 1980; 287: 795–801. - PubMed
-
- Tsukamoto AS, Grosschedl R, Guzman RC, Parslow T, Varmus HE. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell 1988; 55: 619–625. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, van Ooyen A, Cox D, Fung YK, Varmus H. Mode of proviral activation of a putative mammary oncogene (int-1) on mouse chromosome 15. Nature 307: 131–136. - PubMed
-
- Nusse R, Varmus HE. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell 1982; 31: 99–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

