An Inherited Genetic Variant in CEP72 Promoter Predisposes to Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- PMID: 27618250
- PMCID: PMC5320866
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.506
An Inherited Genetic Variant in CEP72 Promoter Predisposes to Vincristine-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
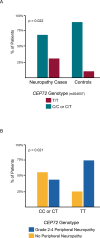
Peripheral neuropathy is a major toxicity of vincristine, yet no strategies exist for identifying adult patients at high-risk. We used a case-control design of 48 adults receiving protocol therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who developed vincristine-induced neuropathy (NCI grade 2-4) during treatment, and 48 matched controls who did not develop grade 2-4 neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy was prospectively graded by National Cancer Institute (NCI) criteria. CEP72 promoter genotype (rs924607) was determined using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping. Frequency of the CEP72 T/T genotype was higher in cases (31% vs. 10%, P = 0.0221) and the incidence of vincristine-induced neuropathy (grades 2-4) was significantly higher in patients homozygous for the CEP72 T/T genotype. 75% of the 20 patients homozygous for the CEP72 T allele developed grade 2-4 neuropathy, compared to 44% of patients with CEP72 CC or CT genotype (P = 0.0221). The CEP72 polymorphism can identify adults at increased risk of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy.
© 2016 American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Pui CH, Evans WE. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 1998;339(9):605–15. - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Evans WE. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The New England journal of medicine. 2006;354(2):166–78. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MA, Wilson L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nature reviews Cancer. 2004;4(4):253–65. - PubMed
-
- Larson RA, Dodge RK, Burns CP, Lee EJ, Stone RM, Schulman P, et al. A five-drug remission induction regimen with intensive consolidation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cancer and leukemia group B study 8811. Blood. 1995;85(8):2025–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA196171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA036401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180888/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA015488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM092666/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM115279/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

