Trans-ancestry meta-analyses identify rare and common variants associated with blood pressure and hypertension
- PMID: 27618447
- PMCID: PMC5056636
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3654
Trans-ancestry meta-analyses identify rare and common variants associated with blood pressure and hypertension
Abstract
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and premature death. However, there is limited knowledge on specific causal genes and pathways. To better understand the genetics of blood pressure, we genotyped 242,296 rare, low-frequency and common genetic variants in up to 192,763 individuals and used ∼155,063 samples for independent replication. We identified 30 new blood pressure- or hypertension-associated genetic regions in the general population, including 3 rare missense variants in RBM47, COL21A1 and RRAS with larger effects (>1.5 mm Hg/allele) than common variants. Multiple rare nonsense and missense variant associations were found in A2ML1, and a low-frequency nonsense variant in ENPEP was identified. Our data extend the spectrum of allelic variation underlying blood pressure traits and hypertension, provide new insights into the pathophysiology of hypertension and indicate new targets for clinical intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests N. P. has received financial support from several pharmaceutical companies that manufacture either blood pressure lowering or lipid lowering agents, or both, and consultancy fees. S. K. has received Research Grant-Merck, Bayer, Aegerion; SAB-Catabasis, Regeneron Genetics Center, Merck, Celera; Equity-San Therapeutics, Catabasis; Consulting-Novartis, Aegerion, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Alnylam. P. Sever has received research awards from Pfizer Inc. A. Malarstig and M. Uria-Nickelsen are full time employees of Pfizer. D. Reily and M. Hoek are full time employees of Merck and co Inc. M.J. Caulfield is Chief Scientist for Genomics England a UK Government company. The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
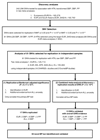
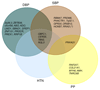
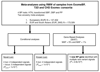
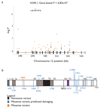
Comment in
-
Genetics: Genetic factors in the regulation of blood pressure.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Dec;12(12):716-717. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.150. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27748393 No abstract available.
References
-
- Munroe PB, Barnes MR, Caulfield MJ. Advances in blood pressure genomics. Circ Res. 2013;112:1365–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085545/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 100114/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0700931/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK072193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085584/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0902313/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL109946/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0600705/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK093757/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 MH083268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT098381/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085501/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RG/15/15/31742/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G1002319/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U106179471/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/04/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- SP/08/005/25115/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL107816/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/02/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/02/128/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL127564/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT098017/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 LM010098/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L01341X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0601966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH063706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K026992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00002/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT091310/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK088389/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL094535/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G9521010D/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SP/10/6/28562/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CZD/16/6/4/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK085526/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/005/23633/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0500539/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 HG000024/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006584/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 086596/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 085475/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG/14/5/30893/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HL087679/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- FS/14/66/31293/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R01 HD057194/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007055/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 098051/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0600237/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12013/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 084723/Z/08/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- SP/09/002/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G0802782/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- G0800270/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

