Comparative effectiveness of immunosuppressive drugs and corticosteroids for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 27619512
- PMCID: PMC5020478
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-016-0328-z
Comparative effectiveness of immunosuppressive drugs and corticosteroids for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: There is a lack of high-quality meta-analyses and network meta-analyses of immunosuppressive drugs for lupus nephritis. Our objective was to assess the comparative benefits and harms of immunosuppressive drugs and corticosteroids in lupus nephritis.
Methods: We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) of trials of immunosuppressive drugs and corticosteroids in patients with lupus nephritis. We calculated odds ratios (OR) and 95 % credible intervals (CrI).
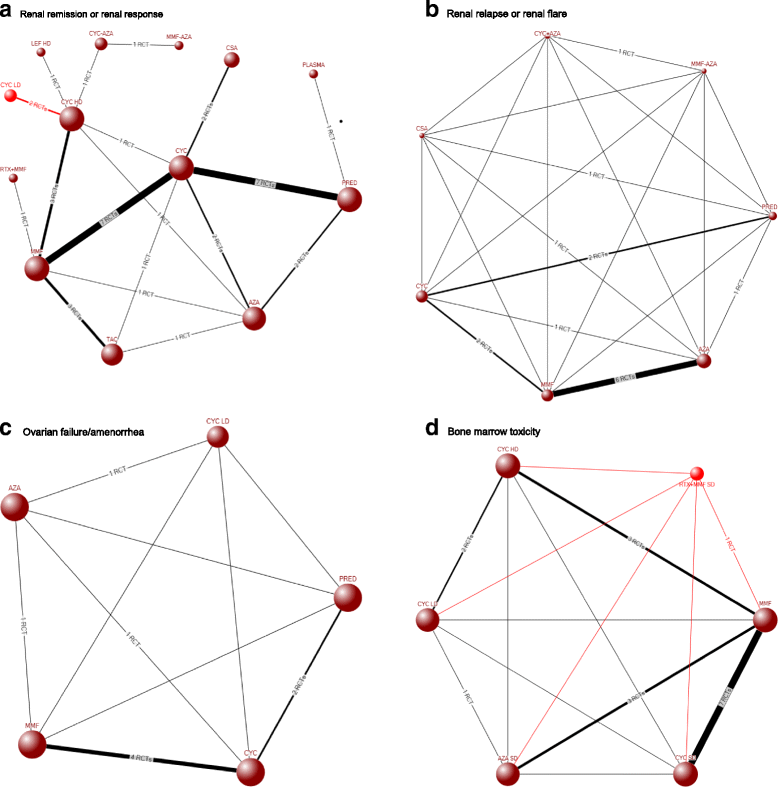
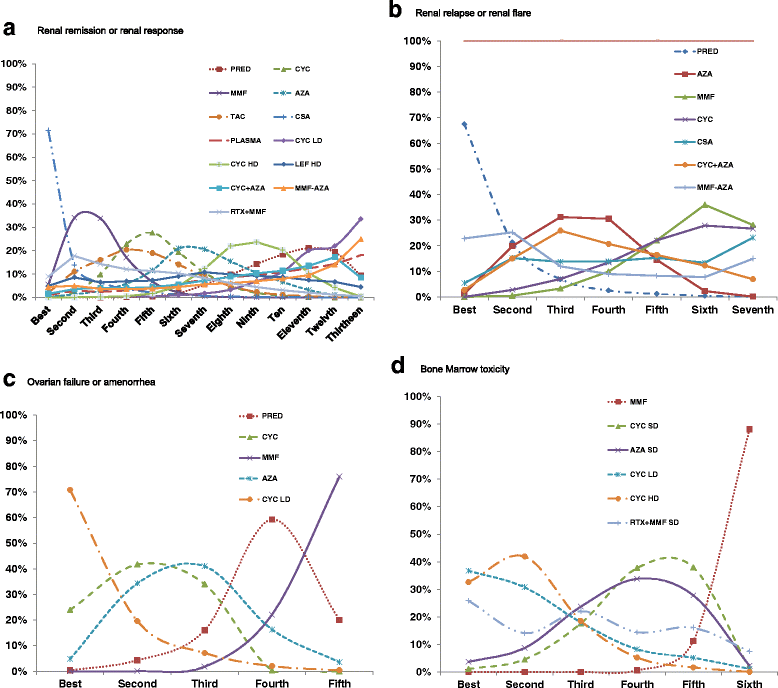
Results: Sixty-five studies that met inclusion and exclusion criteria; data were analyzed for renal remission/response (37 trials; 2697 patients), renal relapse/flare (13 studies; 1108 patients), amenorrhea/ovarian failure (eight trials; 839 patients) and cytopenia (16 trials; 2257 patients). Cyclophosphamide [CYC] low dose (LD) and CYC high-dose (HD) were less likely than mycophenolate mofetil [MMF] and azathioprine [AZA], CYC LD, CYC HD and plasmapharesis less likely than cyclosporine [CSA] to achieve renal remission/response. Tacrolimus [TAC] was more likely than CYC LD to achieve renal remission/response. MMF and CYC were associated with a lower odds of renal relapse/flare compared to PRED and MMF was associated with a lower rate of renal relapse/flare than AZA. CYC was more likely than MMF and PRED to be associated with amenorrhea/ovarian failure. Compared to MMF, CYC, AZA, CYC LD, and CYC HD were associated with a higher risk of cytopenia.
Conclusions: In this systematic review and NMA, we found important differences between immunosuppressives used for the treatment of lupus nephritis. Patients and physicians can use this information for detailed informed consent in a patient-centered approach. Study limitations of between-study clinical heterogeneity and small sample size with type II error must be considered when interpreting these findings.
Prospero: CRD42016032965.
Keywords: Cyclophosphamide; Glucocorticoids; Immunosuppressive drugs; Lupus; Lupus nephritis; Mycophenolate mofetil; Network meta-analysis; Renal relapse; Renal remission; Tacrolimus.
Figures
References
-
- Odutola J, Ward MM. Ethnic and socioeconomic disparities in health among patients with rheumatic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17(2):147–52. doi: 10.1097/01.bor.0000151403.18651.de. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alarcon GS, Friedman AW, Straaton KV, Moulds JM, Lisse J, Bastian HM, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups: III. A comparison of characteristics early in the natural history of the LUMINA cohort. LUpus in MInority populations: NAture vs. Nurture. Lupus. 1999;8(3):197–209. doi: 10.1191/096120399678847704. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Trends in deaths from systemic lupus erythematosus--United States, 1979-1998. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2002;51(17):371-4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

