Carbon dioxide insufflation in esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection reduces mediastinal emphysema: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
- PMID: 27621583
- PMCID: PMC4997641
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i32.7373
Carbon dioxide insufflation in esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection reduces mediastinal emphysema: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial
Abstract
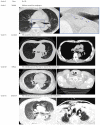
Aim: To assess the efficacy of CO2 insufflation for reduction of mediastinal emphysema (ME) immediately after endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
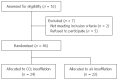
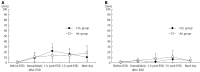
Methods: A total of 46 patients who were to undergo esophageal ESD were randomly assigned to receive either CO2 insufflation (CO2 group, n = 24) or air insufflation (Air group, n = 22). Computed tomography (CT) was carried out immediately after ESD and the next morning. Pain and abdominal distention were chronologically recorded using a 100-mm visual analogue scale (VAS). The volume of residual gas in the digestive tract was measured using CT imaging.
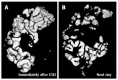
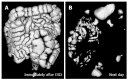
Results: The incidence of ME immediately after ESD in the CO2 group was significantly lower than that in the Air group (17% vs 55%, P = 0.012). The incidence of ME the next morning was 8.3% vs 32% respectively (P = 0.066). There were no differences in pain scores or distention scores at any post-procedure time points. The volume of residual gas in the digestive tract immediately after ESD was significantly smaller in the CO2 group than that in the Air group (808 mL vs 1173 mL, P = 0.013).
Conclusion: CO2 insufflation during esophageal ESD significantly reduced postprocedural ME. CO2 insufflation also reduced the volume of residual gas in the digestive tract immediately after ESD, but not the VAS scores of pain and distention.
Keywords: Carbon dioxide insufflation; Complication; Endoscopic submucosal dissection; Mediastinal emphysema; Superficial esophageal cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Dellon ES, Hawk JS, Grimm IS, Shaheen NJ. The use of carbon dioxide for insufflation during GI endoscopy: a systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:843–849. - PubMed
-
- Sumanac K, Zealley I, Fox BM, Rawlinson J, Salena B, Marshall JK, Stevenson GW, Hunt RH. Minimizing postcolonoscopy abdominal pain by using CO(2) insufflation: a prospective, randomized, double blind, controlled trial evaluating a new commercially available CO(2) delivery system. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:190–194. - PubMed
-
- Maple JT, Keswani RN, Hovis RM, Saddedin EZ, Jonnalagadda S, Azar RR, Hagen C, Thompson DM, Waldbaum L, Edmundowicz SA. Carbon dioxide insufflation during ERCP for reduction of postprocedure pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:278–283. - PubMed
-
- Domagk D, Bretthauer M, Lenz P, Aabakken L, Ullerich H, Maaser C, Domschke W, Kucharzik T. Carbon dioxide insufflation improves intubation depth in double-balloon enteroscopy: a randomized, controlled, double-blind trial. Endoscopy. 2007;39:1064–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

