Screening of Rhizospheric Actinomycetes for Various In-vitro and In-vivo Plant Growth Promoting (PGP) Traits and for Agroactive Compounds
- PMID: 27621724
- PMCID: PMC5002418
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01334
Screening of Rhizospheric Actinomycetes for Various In-vitro and In-vivo Plant Growth Promoting (PGP) Traits and for Agroactive Compounds
Abstract
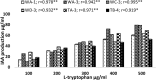
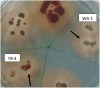
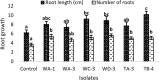
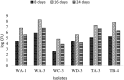
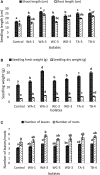
In this study 98 rhizospheric actinomycetes were isolated from different wheat and tomato fields, Punjab, Pakistan. The isolates were characterized morphologically, biochemically, and genetically and were subjected to a comprehensive in vitro screening for various plant growth promoting (PGP) traits. About 30% of the isolates screened were found to be the promising PGP rhizobacteria (PGPRs), which exhibited maximum genetic similarity (up to 98-99%) with different species of the genus Streptomyces by using16S rRNA gene sequencing. The most active indole acetic acid (IAA) producer Streptomyces nobilis WA-3, Streptomyces Kunmingenesis WC-3, and Streptomyces enissocaesilis TA-3 produce 79.5, 79.23, and 69.26 μg/ml IAA respectively at 500 μg/ml L-tryptophan. The highest concentration of soluble phosphate was produced by Streptomyces sp. WA-1 (72.13 mg/100 ml) and S. djakartensis TB-4 (70.36 mg/100 ml). All rhizobacterial isolates were positive for siderophore, ammonia, and hydrogen cyanide production. Strain S. mutabilis WD-3 showed highest concentration of ACC-deaminase (1.9 mmol /l). For in-vivo screening, seed germination, and plant growth experiment were conducted by inoculating wheat (Triticum aestivum) seeds with the six selected isolates. Significant increases in shoot length was observed with S. nobilis WA-3 (65%), increased root length was recorded in case of S. nobilis WA-3 (81%) as compared to water treated control plants. Maximum increases in plant fresh weight were recorded with S. nobilis WA-3 (84%), increased plant dry weight was recorded in case of S. nobilis WA-3 (85%) as compared to water treated control plants. In case of number of leaves, significant increase was recorded with S. nobilis WA-3 (27%) and significant increase in case of number of roots were recorded in case of strain S. nobilis WA-3 (30%) as compared to control plants. Over all the study revealed that these rhizospheric PGP Streptomyces are good candidates to be developed as bioferlizers for growth promotion and yield enhancement in wheat crop and can be exploited for the commercial production of different agro-active compounds.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene sequencing; agro-active compounds; biofertilizers; indole acetic acid (IAA); plant growth promoting Streptomyces; wheat.
Figures
References
-
- Abd-Alla M. H., El-Sayed E. S. A., Rasmey A. H. M. (2013). Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) production by Streptomyces atrovirens. J. Biol. Earth Sci. 3, 82–93.
-
- Akhtar M. J., Asghar H. N., Shahzad K., Arshad M. (2009). Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria applied in combination with compost and mineral fertilizers to improve growth and yield of wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.). Pak. J. Bot. 41, 381–390.
-
- Alexander D. B., Zuberer D. A. (1991). Use of Chrome Azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria Biol. Fertility Soils. 12, 39–45. 10.1007/BF00369386 - DOI
-
- Alexander M. (1977). Introduction to Soil Microbiology. 2nd Edn., Malabar, FL: Krieger Publishing Company.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

