Integration of suboptimal health status and endothelial dysfunction as a new aspect for risk evaluation of cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 27621756
- PMCID: PMC5018938
- DOI: 10.1186/s13167-016-0068-0
Integration of suboptimal health status and endothelial dysfunction as a new aspect for risk evaluation of cardiovascular disease
Abstract
Background: Suboptimal health status (SHS) is recognized as a subclinical, reversible stage of chronic disease. Association has been confirmed between SHS and cardiovascular risk factors, indicating that SHS may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. This study explored integrated risk assessment of cardiovascular disease by combining SHS questionnaire-25 (SHSQ-25) and indicators of endothelial dysfunction.
Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted in a sample of 459 residents of Samara, Russia, who had no history of clinical diagnosed disease and did not receive any treatment in the last 2 weeks. The SHS score was derived from the data collected in the SHSQ-25. Blood pressure, body mass index, and glucose and lipid levels (total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein, cholesterol and triglycerides) were measured by physical examination and laboratory performance. The relationship between SHS and endothelial dysfunction was examined using Pearson's correlation linear regression analysis. Cluster analysis was performed to identify systemic patterns arising from exposure to a variety of risk factors.
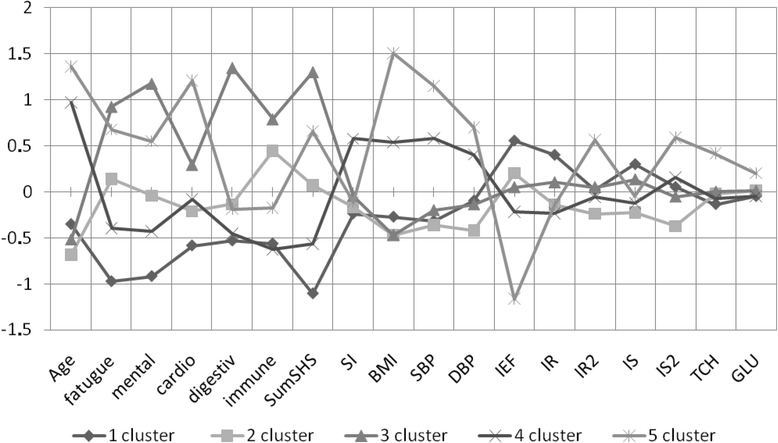
Results: Significant correlations were observed between index of endothelial function and the overall performance of SHS (r = -0.31, p < 0.05), and individual scales of the questionnaire SHSQ-25: fatigue (r = -0.36, p < 0.05), mental (r = -0.29, p < 0.05), and the cardiovascular system (r = -0.36). Based on cluster analysis, all subjects were grouped into five clusters: (1) optimal health status, (2) SHS at low risk of disease states, (3) SHS with a high risk of non-cardiac pathologies profile, (4) SHS of low risk of cardiovascular disease, and (5) SHS with high risk of cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions: SHS is associated with endothelial dysfunction. Integration of suboptimal health status and endothelial dysfunction provides a novel tool to allow people to get a more holistic picture of both subjective and objective health measures, and also can be applied to routine screening for risks of cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Endothelial dysfunction; Risk factors; Suboptimal health status.
Figures
References
-
- Shalnova SA, Konradi AO, Karpov YA, Kontsevaya AV, Deev AD, Kapustina AV, et al. Cardiovascular mortality in 12 Russian Federation regions—participants of the “Cardiovascular Disease epidemiology in Russian Regions” study. Russ J Cardiol. 2012;5:6–11.
-
- Oganov RG, Pogosova GV. Sovremennye strategii profilaktiki I lechenija serdechno- sosudistyh zabolevanij. Kardiologija (Cardiology) 2007;12:4–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

