Erythroblast transformation-specific 2 correlates with vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in rat heterotopic heart transplantation model
- PMID: 27621856
- PMCID: PMC4999686
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2016.07.24
Erythroblast transformation-specific 2 correlates with vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis in rat heterotopic heart transplantation model
Abstract
Background: Cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV) decreases the long-term survival of heart transplantation recipients. Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) apoptosis is an important pathological feature of CAV. Erythroblast transformation-specific 2 (Ets-2), as a transcription factor, participates in cell apoptosis and plays an important role in organ transplantation.
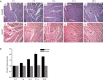
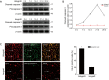
Methods: Hearts from Wistar-Furth (WF:RT1u) rats were heterotopically transplanted into Lewis (Lew:RT1(l)) rats without immunosuppression. Additional syngeneic heterotopic cardiac transplantations were performed in Lewis rats. HE staining was used to identify CAV. Ets-2 expression was examined by western blot. Ets-2 tissue location was examined by immunohistochemical assay and double immunostaining. Cleaved caspase 3 expression was detected by western blot. Co-localization of Ets-2 and cleaved caspase 3 was detected by double immunostaining. Ets-2, p53, cleaved caspase 3 and Bcl-xl expression in rat VSMC line A7R5 was examined after Ets-2 siRNA transfection. TUNEL assay was applied to detect A7R5 apoptosis with or without ETS-2 siRNA transfection. Immunoprecipitation was performed to explore the interaction between Ets-2 and p53.
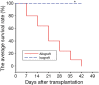
Results: Ets-2 expression decreased in the allograft group but had no obvious change in the isograft group. Meanwhile, the phenomenon of CAV was observed in the allograft group and there is neointima formation in the isograft group which is not obvious compared with allograft group. Additionally, Ets-2 expression was opposite to VSMC apoptosis in the allograft group. In vitro, Ets-2 siRNA transfection in A7R5cells resulted in enhanced cell apoptosis. Finally, Ets-2 interacted with p53.
Conclusions: Ets-2 might inhibit VSMC apoptosis via p53 pathway. The results further elucidate the molecular mechanism of VSMC apoptosis after heart transplantation during CAV and provide theoretical basis for seeking new specific drug targets for CAV prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Cardiac transplantation; cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV); erythroblast transformation-specific 2 (Ets-2); vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis (VSMC apoptosis).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MMP-14 promotes VSMC migration via up-regulating CD44 expression in cardiac allograft vasculopathy.Pathol Res Pract. 2016 Dec;212(12):1119-1125. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Pathol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27712978
-
Cardiomyocyte-targeted HIF-1alpha gene therapy inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and cardiac allograft vasculopathy in the rat.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010 Sep;29(9):1058-66. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2010.05.021. Epub 2010 Jun 26. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20580263
-
The changes of vaccinia related kinase 1 in grafted heart after rat heart transplantation.J Thorac Dis. 2014 Dec;6(12):1742-50. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.11.17. J Thorac Dis. 2014. PMID: 25589968 Free PMC article.
-
European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging/Cardiovascular Imaging Department of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology recommendations for the use of cardiac imaging to assess and follow patients after heart transplantation.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Sep;16(9):919-48. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev139. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26139361 Review.
-
Impact of immunosuppressive drugs on the development of cardiac allograft vasculopathy.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;8(5):706-19. doi: 10.2174/157016110792006923. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20649510 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
