Proof of concept study with an HER-2 mimotope anticancer vaccine deduced from a novel AAV-mimotope library platform
- PMID: 27622022
- PMCID: PMC5006910
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1171446
Proof of concept study with an HER-2 mimotope anticancer vaccine deduced from a novel AAV-mimotope library platform
Abstract
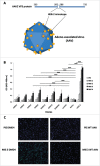
Background: Anticancer vaccines could represent a valuable complementary strategy to established therapies, especially in settings of early stage and minimal residual disease. HER-2 is an important target for immunotherapy and addressed by the monoclonal antibody trastuzumab. We have previously generated HER-2 mimotope peptides from phage display libraries. The synthesized peptides were coupled to carriers and applied for epitope-specific induction of trastuzumab-like IgG. For simplification and to avoid methodological limitations of synthesis and coupling chemistry, we herewith present a novel and optimized approach by using adeno-associated viruses (AAV) as effective and high-density mimotope-display system, which can be directly used for vaccination.
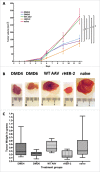
Methods: An AAV capsid display library was constructed by genetically incorporating random peptides in a plasmid encoding the wild-type AAV2 capsid protein. AAV clones, expressing peptides specifically reactive to trastuzumab, were employed to immunize BALB/c mice. Antibody titers against human HER-2 were determined, and the isotype composition and functional properties of these were tested. Finally, prophylactically immunized mice were challenged with human HER-2 transfected mouse D2F2/E2 cells.
Results: HER-2 mimotope AAV-vaccines induced antibodies specific to human HER-2. Two clones were selected for immunization of mice, which were subsequently grafted D2F2/E2 cells. Both mimotope AAV clones delayed the growth of tumors significantly, as compared to controls.
Conclusion: In this study, a novel mimotope AAV-based platform was created allowing the isolation of mimotopes, which can be directly used as anticancer vaccines. The example of trastuzumab AAV-mimotopes demonstrates that this vaccine strategy could help to establish active immunotherapy for breast-cancer patients.
Keywords: AAV; HER-2; adeno-associated virus; cancer vaccine; mimotope.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of Peptide mimics of the epitope recognized by trastuzumab on the oncogenic protein Her-2/neu.J Immunol. 2004 Jul 1;173(1):394-401. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.1.394. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15210798
-
Identification of anti-CD98 antibody mimotopes for inducing antibodies with antitumor activity by mimotope immunization.Cancer Sci. 2014 Apr;105(4):396-401. doi: 10.1111/cas.12365. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24484217 Free PMC article.
-
Active induction of tumor-specific IgE antibodies by oral mimotope vaccination.Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1;67(7):3406-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3758. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17409451
-
Mimotope vaccination--from allergy to cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009 Apr;9(4):493-506. doi: 10.1517/14712590902870386. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19344285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage display peptide libraries in molecular allergology: from epitope mapping to mimotope-based immunotherapy.Allergy. 2016 Nov;71(11):1526-1532. doi: 10.1111/all.12965. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Allergy. 2016. PMID: 27341497 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Vaccination with B Cell Peptides Targeting Her-2/neu and Immune Checkpoints as Emerging Treatment Option in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;14(22):5678. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225678. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capsid Modifications for Targeting and Improving the Efficacy of AAV Vectors.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019 Jan 26;12:248-265. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.01.008. eCollection 2019 Mar 15. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019. PMID: 30815511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AllergoOncology: High innate IgE levels are decisive for the survival of cancer-bearing mice.World Allergy Organ J. 2019 Jul 29;12(7):100044. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2019.100044. eCollection 2019. World Allergy Organ J. 2019. PMID: 31388397 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous Prime-Boost Enhances the Antitumor Immune Response Elicited by Plant-Virus-Based Cancer Vaccine.J Am Chem Soc. 2019 Apr 24;141(16):6509-6518. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01523. Epub 2019 Apr 16. J Am Chem Soc. 2019. PMID: 30995022 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled peptide and protein nanostructures for anti-cancer therapy: Targeted delivery, stimuli-responsive devices and immunotherapy.Nano Today. 2021 Jun;38:101119. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101119. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Nano Today. 2021. PMID: 34267794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiemann B, Starnes CO. Coley's toxins, tumor necrosis factor and cancer research: a historical perspective. Pharmacol Ther 1994; 64:529-64; PMID:7724661; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/0163-7258(94)90023-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsung K, Norton JA. Lessons from Coley's toxin. Surg Oncol 2006; 15:25-8; PMID:16814541; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.suronc.2006.05.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12:278-87; PMID:22437872; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nrc3236 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DM, Schrump DS. Growth factor receptors as targets for lung cancer therapy. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004; 16:3-12; PMID:15366682; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2003.12.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
