The Clinical Usefulness of Tuberculin Skin Test versus Interferon-Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis in HIV Patients: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27622293
- PMCID: PMC5021339
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161983
The Clinical Usefulness of Tuberculin Skin Test versus Interferon-Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis in HIV Patients: A Meta-Analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: The Clinical Usefulness of Tuberculin Skin Test versus Interferon-Gamma Release Assays for Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis in HIV Patients: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 18;11(10):e0165143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165143. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27755606 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Accurate diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) is becoming increasingly concerning due to the increasing the HIV epidemic, which have increased the risk for reactivation to active tuberculosis (TB) infection. LTBI is diagnosed by tuberculin skin test (TST) and interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs).
Objectives: The aim of the present study was to conduct a meta-analysis of published papers on the agreement (kappa) between TST and QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube (QFT-GIT) tests for diagnosis of LTBI in HIV patient.
Methods: Electronic databases including PubMed/Medline, Elsevier/Scopus and Embase/Ovid were reviewed up Jan. 2016. We performed a random effect model meta-analysis for estimation of pooled Kappa between the two methods of diagnosis. Meta regression was used for assessing potential heterogeneity and Egger's test was used for assessing small study effect and publication bias.
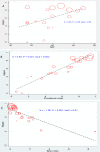
Results: The initial search strategy produced 6744 records. Of them, 23 cross-sectional studies met the inclusion criteria and 20 studies entered in meta-analysis. The pooled kappa was and prevalence-adjusted and bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) were 0.37 (95% CI: 0.28, 0.46) and 0.59 (0.49, 0.69). The discordance of TST-/QFT-GIT+ was more than TST+/QFT-GIT-. Kappa estimate between two tests was linearly associated with age and prevalence index and inversely associated with bias index.
Conclusion: Fair agreement between TST and QFT-GIT makes it difficult to know whether TST is as useful as the QFT-GIT in HIV-infected patients. The higher discordance of TST-/QFT-GIT+ in compared to TST+/QFT-GIT- can induce the higher sensitivity of QFT-GIT for diagnosis LTBI in HIV patients. Disagreement between two tests can be influenced by error in measurements and prevalence of HIV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization, Geneva: Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2014: World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- World Health Organization, Geneva: Global tuberculosis control: WHO report 2012. 2012.
-
- Taylor Z, Nolan CM, Blumberg HM. Controlling tuberculosis in the United States. Recommendations from the American Thoracic Society, CDC, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMWR Recommendations and reports: Morbidity and mortality weekly report Recommendations and reports/Centers for Disease Control. 2005;54(RR-12):1–81. - PubMed
-
- Farhat M, Greenaway C, Pai M, Menzies D. False-positive tuberculin skin tests: what is the absolute effect of BCG and non-tuberculous mycobacteria?[Review Article]. The International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 2006;10(11):1192–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

