A Novel High-Throughput 3D Screening System for EMT Inhibitors: A Pilot Screening Discovered the EMT Inhibitory Activity of CDK2 Inhibitor SU9516
- PMID: 27622654
- PMCID: PMC5021355
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162394
A Novel High-Throughput 3D Screening System for EMT Inhibitors: A Pilot Screening Discovered the EMT Inhibitory Activity of CDK2 Inhibitor SU9516
Abstract
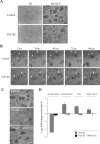
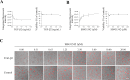
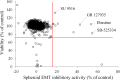
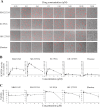
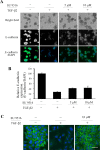
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a crucial pathological event in cancer, particularly in tumor cell budding and metastasis. Therefore, control of EMT can represent a novel therapeutic strategy in cancer. Here, we introduce an innovative three-dimensional (3D) high-throughput screening (HTS) system that leads to an identification of EMT inhibitors. For the establishment of the novel 3D-HTS system, we chose NanoCulture Plates (NCP) that provided a gel-free micro-patterned scaffold for cells and were independent of other spheroid formation systems using soft-agar. In the NCP-based 3D cell culture system, A549 lung cancer cells migrated, gathered, and then formed multiple spheroids within 7 days. Live cell imaging experiments showed that an established EMT-inducer TGF-β promoted peripheral cells around the core of spheroids to acquire mesenchymal spindle shapes, loss of intercellular adhesion, and migration from the spheroids. Along with such morphological change, EMT-related gene expression signatures were altered, particularly alteration of mRNA levels of ECAD/CDH1, NCAD/CDH2, VIM and ZEB1/TCF8. These EMT-related phenotypic changes were blocked by SB431542, a TGF-βreceptor I (TGFβR1) inhibitor. Inside of the spheroids were highly hypoxic; in contrast, spheroid-derived peripheral migrating cells were normoxic, revealed by visualization and quantification using Hypoxia Probe. Thus, TGF-β-triggered EMT caused spheroid hypoplasia and loss of hypoxia. Spheroid EMT inhibitory (SEMTIN) activity of SB431542 was calculated from fluorescence intensities of the Hypoxia Probe, and then was utilized in a drug screening of EMT-inhibitory small molecule compounds. In a pilot screening, 9 of 1,330 compounds were above the thresholds of the SEMTIN activity and cell viability. Finally, two compounds SB-525334 and SU9516 showed SEMTIN activities in a dose dependent manner. SB-525334 was a known TGFβR1 inhibitor. SU9516 was a cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) inhibitor, which we showed also had an EMT-inhibitory activity. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of SB-525334 and SU9516 were 0.31 μM and 1.21 μM, respectively, while IC50 of SB431542 was 2.38 μM. Taken together, it was shown that this 3D NCP-based HTS system was useful for screening of EMT-regulatory drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
Kazuya Arai, M Mamunur Rahman, Ruriko Sakamoto, Norio Masuda and Manabu Itoh are employed by SCIVAX Life Sciences Inc. (currently, ORGANOGENIX, Inc.). There are no patents, products in development or marketed products to declare. This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials, as detailed online in the guide for authors.
Figures


References
-
- Kim JB, Stein R, O'hare MJ. Three-dimensional in vitro tissue culture models of breast cancer—a review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 85(3):281–91. - PubMed
-
- Zang R, Li D, Tang IC, Wang J, Yang ST. Cell-based assays in high-throughput screening for drug discovery. Int J Biotechnol Wellness Ind. 2012; 1(1), 31–51.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

