Pits, a protein interacting with Ttk69 and Sin3A, has links to histone deacetylation
- PMID: 27622813
- PMCID: PMC5020733
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33388
Pits, a protein interacting with Ttk69 and Sin3A, has links to histone deacetylation
Abstract
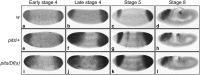
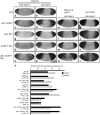
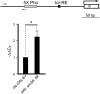
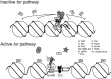
Histone deacetylation plays an important role in transcriptional repression. Previous results showed that the genetic interaction between ttk and rpd3, which encodes a class I histone deacetylase, is required for tll repression. This study investigated the molecular mechanism by which Ttk69 recruits Rpd3. Using yeast two-hybrid screening and datamining, one novel protein was found that weakly interacts with Ttk69 and Sin3A, designated as Protein interacting with Ttk69 and Sin3A (Pits). Pits protein expressed in the early stages of embryos and bound to the region of the tor response element in vivo. Expanded tll expression patterns were observed in embryos lacking maternal pits activity and the expansion was not widened by reducing either maternal ttk or sin3A activity. However, in embryos with simultaneously reduced maternal pits and sin3A activities or maternal pits, sin3A and ttk activities, the proportions of the embryos with expanded tll expression were significantly increased. These results indicate that all three gene activities are involved in tll repression. Level of histone H3 acetylation in the tll proximal region was found to be elevated in embryo with reduced these three gene activities. In conclusion, Ttk69 causes the histone deacetylation-mediated repression of tll via the interaction of Pits and Sin3A.
Figures
References
-
- Narlikar G. J., Fan H. Y. & Kingston R. E. Cooperation between complexes that regulate chromatin structure and transcription. Cell 108, 475–487 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

