Reelin Regulates the Maturation of Dendritic Spines, Synaptogenesis and Glial Ensheathment of Newborn Granule Cells
- PMID: 27624722
- PMCID: PMC5066826
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhw216
Reelin Regulates the Maturation of Dendritic Spines, Synaptogenesis and Glial Ensheathment of Newborn Granule Cells
Abstract
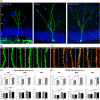
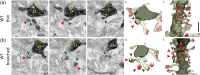
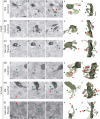
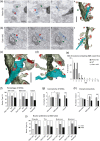
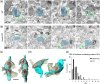
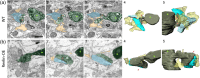
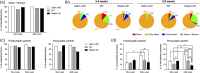
The extracellular protein Reelin has an important role in neurological diseases, including epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease and psychiatric diseases, targeting hippocampal circuits. Here we address the role of Reelin in the development of synaptic contacts in adult-generated granule cells (GCs), a neuronal population that is crucial for learning and memory and implicated in neurological and psychiatric diseases. We found that the Reelin pathway controls the shapes, sizes, and types of dendritic spines, the complexity of multisynaptic innervations and the degree of the perisynaptic astroglial ensheathment that controls synaptic homeostasis. These findings show a pivotal role of Reelin in GC synaptogenesis and provide a foundation for structural circuit alterations caused by Reelin deregulation that may occur in neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: 3D-electron microscopy; FIB/SEM; adult neurogenesis; axospinous synapses; glia.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


References
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, Shafa R, Glatt SJ, Nguyen G, Ponte JF, et al. . 2005. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 134B:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL, Wheeler AL, Guskjolen A, Niibori Y, Shoji H, et al. . 2014. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science. 344:598–602. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

