Expression and Clinical Significance of Cytokeratin-19 and Thymidine Kinase-1 in Advanced Gastrointestinal Cancer
- PMID: 27625087
- PMCID: PMC5022336
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.189919
Expression and Clinical Significance of Cytokeratin-19 and Thymidine Kinase-1 in Advanced Gastrointestinal Cancer
Abstract
Background: As the clinical value of cytokeratin-19 (CK19) and thymidine kinase-1 (TK1) in advanced gastrointestinal cancer remains controversial, we investigated their expression and clinical significance in this disease.
Methods: A total of 171 advanced gastrointestinal cancer patients were prospectively enrolled in this study. The mRNA level of CK19 was detected using quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in all patients, along with a control group of fifty healthy individuals. Furthermore, detection of TK1 protein was carried out in 96 patients using a chemiluminescence dot blot assay. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS) time.
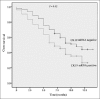
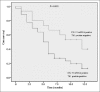
Results: Positive CK19 mRNA expression was detected in 74 (43.3%) of the 171 patients and positive TK1 expression was detected in 66 (68.8%) of the 96 patients. Furthermore, of the 96 patients, 36 (37.5%) were positive for both TK1 protein and CK19 mRNA, 30 (31.3%) were negative for TK1 protein, and 15 (15.6%) were negative for TK1 protein and positive for CK19 mRNA. The results indicated that patients who were positive for CK19 mRNA expression had significantly shorter OS times than those who were negative for it (median OS 7.7 vs. 9.7 months, respectively; P = 0.02). Moreover, patients who were positive for CK19 mRNA and TK1 protein expression had shorter OS times (median OS 6.1 months) than those who were positive for CK19 mRNA and negative for TK1 protein expression (median OS 9.1 months; P = 0.028). Positive CK19 mRNA expression was significantly associated with shorter OS in the univariate analysis (P = 0.027). Based on a multivariate Cox regression analysis, CK19 mRNA together with TK1 protein expression (P = 0.024) was an independent predictor for OS in gastrointestinal cancer patients.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that positive expression of CK19 mRNA and TK1 protein is closely correlated with poor prognosis in advanced gastrointestinal cancer. Furthermore, both CK19 and TK1 are possible gastrointestinal cancer biomarkers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of preoperative and postoperative CK19 and CEA mRNA levels in peripheral blood of patients with gastric cardia cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb 28;23(8):1424-1433. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i8.1424. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28293089 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow cytokeratin 19 mRNA level is an independent predictor of relapse-free survival in operable breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Mar;108(2):251-8. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9592-x. Epub 2007 May 10. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 17492378 Clinical Trial.
-
CK19 mRNA expression measured by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in the peripheral blood of patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated by chemo-radiation: an independent prognostic factor.Lung Cancer. 2007 Apr;56(1):105-14. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.11.006. Epub 2006 Dec 12. Lung Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17166620
-
Thymidine kinase 1 as a tumor biomarker: technical advances offer new potential to an old biomarker.Biomark Med. 2018 Sep;12(9):1035-1048. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2018-0157. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Biomark Med. 2018. PMID: 30039979 Review.
-
TK1 overexpression is associated with the poor outcomes of lung cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomark Med. 2018 Apr;12(4):403-413. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2017-0249. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Biomark Med. 2018. PMID: 29575921
Cited by
-
Clinical Significance and Role of TK1, CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 levels in Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancers.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Nov 1;21(11):3133-3136. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.11.3133. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 33247667 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Biomarkers Correlated with the TNM Staging and Overall Survival of Patients with Bladder Cancer.Front Physiol. 2017 Nov 28;8:947. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00947. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29234286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayes DF, Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A, Miller MC, et al. Circulating tumor cells at each follow-up time point during therapy of metastatic breast cancer patients predict progression-free and overall survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:4218–24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2821. - PubMed
-
- Reinholz MM, Kitzmann KA, Tenner K, Hillman D, Dueck AC, Hobday TJ, et al. Cytokeratin-19 and mammaglobin gene expression in circulating tumor cells from metastatic breast cancer patients enrolled in North Central Cancer Treatment Group trials, N0234/336/436/437. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:7183–93. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0981. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

