Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab 150 mg Every 4 Weeks in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia Not on Statin Therapy: The ODYSSEY CHOICE II Study
- PMID: 27625344
- PMCID: PMC5079013
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003421
Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab 150 mg Every 4 Weeks in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia Not on Statin Therapy: The ODYSSEY CHOICE II Study
Abstract
Background: The PCSK9 antibody alirocumab (75 mg every 2 weeks; Q2W) as monotherapy reduced low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels by 47%. Because the option of a monthly dosing regimen is convenient, ODYSSEY CHOICE II evaluated alirocumab 150 mg Q4W in patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolemia and not on statin (majority with statin-associated muscle symptoms), receiving treatment with fenofibrate, ezetimibe, or diet alone.
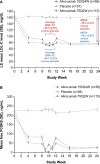
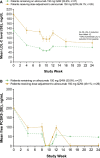
Methods and results: Patients were randomly assigned to placebo, alirocumab 150 mg Q4W or 75 mg Q2W (calibrator arm), with dose adjustment to 150 mg Q2W at week (W) 12 if W8 predefined LDL-C target levels were not met. The primary efficacy endpoint was LDL-C percentage change from baseline to W24. Mean baseline LDL-C levels were 163.9 mg/dL (alirocumab 150 mg Q4W, n=59), 154.5 mg/dL (alirocumab 75 mg Q2W, n=116), and 158.5 mg/dL (placebo, n=58). In the alirocumab 150 mg Q4W and 75 mg Q2W groups (49.1% and 36.0% of patients received dose adjustment, respectively), least-squares mean LDL-C changes from baseline to W24 were -51.7% and -53.5%, respectively (placebo [+4.7%]; both groups P<0.0001 versus placebo). In total, 63.9% and 70.3% of alirocumab-treated patients achieved their LDL-C targets at W24. Treatment-emergent adverse events occurred in 77.6% (alirocumab 150 mg Q4W), 73.0% (alirocumab 75 mg Q2W), and 63.8% (placebo) of patients, with injection-site reactions among the most common treatment-emergent adverse events.
Conclusions: Alirocumab 150 mg Q4W can be considered in patients not on statin with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolemia as a convenient option for lowering LDL-C.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT02023879.
Keywords: alirocumab; cardiovascular risk; low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; placebo‐controlled; proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9.
© 2016 The Authors, Sanofi, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

References
-
- Brugts JJ, Yetgin T, Hoeks SE, Gotto AM, Shepherd J, Westendorp RG, de Craen AJ, Knopp RH, Nakamura H, Ridker P, van Domburg R, Deckers JW. The benefits of statins in people without established cardiovascular disease but with cardiovascular risk factors: meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2009;338:b2376. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reiner Z, Catapano AL, De Backer G, Graham I, Taskinen MR, Wiklund O, Agewall S, Alegria E, Chapman MJ, Durrington P, Erdine S, Halcox J, Hobbs R, Kjekshus J, Filardi PP, Riccardi G, Storey RF, Wood D. ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the Management of Dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1769–1818. - PubMed
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, Goldberg AC, Gordon D, Levy D, Lloyd‐Jones DM, McBride P, Schwartz JS, Shero ST, Smith SC Jr, Watson K, Wilson PW. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2889–2934. - PubMed
-
- Kashani A, Phillips CO, Foody JM, Wang Y, Mangalmurti S, Ko DT, Krumholz HM. Risks associated with statin therapy: a systematic overview of randomized clinical trials. Circulation. 2006;114:2788–2797. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr, Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT, Glynn RJ. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C‐reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2195–2207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

