Associations Between Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 in Plasma and First-Time Coronary Events: A Nested Case-Control Study
- PMID: 27625345
- PMCID: PMC5079003
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002851
Associations Between Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein 1 in Plasma and First-Time Coronary Events: A Nested Case-Control Study
Abstract
Background: Myeloid cells play a central role in atherosclerosis. We investigated the associations between the plasma levels of growth factors and chemokines that regulate myeloid cell homeostasis and function and the risk of first-time acute coronary events in middle-aged persons.
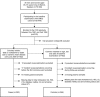
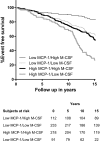
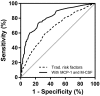
Methods and results: We measured baseline plasma levels of macrophage colony-stimulating factor; monocyte chemotactic protein 1; C-C motif chemokine ligands 3, 4, and 20; C-X-C motif chemokine ligands 1, 6, and 16; and C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1 in 292 participants who had a coronary event during follow-up and 366 controls matched for age, sex, and time of inclusion who remained event free. Study participants were recruited from the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study population cohort and had no previous history of coronary artery disease. We found a strong independent negative association between macrophage colony-stimulating factor and incident coronary events in a forward stepwise Cox proportional hazards model including all biomarkers alongside the classic Framingham risk factors (age, sex, smoking, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, systolic blood pressure), diabetes mellitus, and medication. Conversely, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 had the strongest independent positive association with the outcome. The addition of macrophage colony-stimulating factor and monocyte chemotactic protein 1 significantly improved the predictive ability of a model including traditional risk factors alone (C statistic 0.81 [95% CI 0.78-0.84] versus 0.67 [95% CI 0.63-0.71]; net reclassification index 0.52 [0.42-0.62]; P<0.001). The combined model led to a 54% net downclassification of participants who did not have a coronary event during follow-up and was particularly effective in the intermediate-risk group.
Conclusions: High levels of macrophage colony-stimulating factor and low levels of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in plasma characterize middle-aged persons at low risk to develop clinically manifested coronary artery disease.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; inflammation; innate immunity; leukocytes; macrophage colony‐stimulating factor; monocyte chemotactic protein 1.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma CX3CL1 levels and long term outcomes of patients with atrial fibrillation: the West Birmingham Atrial Fibrillation Project.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;38(3):204-11. doi: 10.1159/000365841. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 25301077
-
Pilot study: elevated circulating levels of the proinflammatory cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with chronic spinal cord injury.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Aug;94(8):1498-507. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 23618747
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor and the risk of myocardial infarction or death due to coronary artery disease in adults without prior myocardial infarction or stroke: the EPIC-Norfolk Prospective Population study.Am J Med. 2004 Sep 15;117(6):390-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.04.010. Am J Med. 2004. PMID: 15380495
-
Kinetics of chemokines in acute myocardial infarction.Kardiol Pol. 2005 Apr;62(4):301-14; discussion 315-6. Kardiol Pol. 2005. PMID: 15928736 English, Polish.
-
Potential clinical utility of macrophage colony-stimulating factor, monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and myeloperoxidase in predicting atherosclerotic plaque instability.Discov Med. 2019 Nov-Dec;28(155):237-245. Discov Med. 2019. PMID: 32053764 Review.
Cited by
-
Leukocyte Trafficking via Lymphatic Vessels in Atherosclerosis.Cells. 2021 May 29;10(6):1344. doi: 10.3390/cells10061344. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34072313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 Jul;16(7):389-406. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0169-2. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30846875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Level of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease: A Case-Control and Mendelian Randomization Study.Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021 May 11;14:553-559. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S303362. eCollection 2021. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34007203 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of food intake on 92 biomarkers for cardiovascular disease.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 6;12(6):e0178656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178656. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28586402 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 and Risk of Stroke: Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies Involving 17 180 Individuals.Circ Res. 2019 Sep 27;125(8):773-782. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315380. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Circ Res. 2019. PMID: 31476962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Doring Y, Drechsler M, Soehnlein O, Weber C. Neutrophils in atherosclerosis: from mice to man. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35:288–295. - PubMed
-
- Zernecke A, Weber C. Chemokines in atherosclerosis: proceedings resumed. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:742–750. - PubMed
-
- Berg KE, Ljungcrantz I, Andersson L, Bryngelsson C, Hedblad B, Fredrikson GN, Nilsson J, Bjorkbacka H. Elevated CD14++CD16‐ monocytes predict cardiovascular events. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012;5:122–131. - PubMed
-
- Cotoi OS, Duner P, Ko N, Hedblad B, Nilsson J, Bjorkbacka H, Schiopu A. Plasma S100A8/A9 correlates with blood neutrophil counts, traditional risk factors, and cardiovascular disease in middle‐aged healthy individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34:202–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

