Smartphone and Universal Goniometer for Measurement of Elbow Joint Motions: A Comparative Study
- PMID: 27625754
- PMCID: PMC5003314
- DOI: 10.5812/asjsm.30668
Smartphone and Universal Goniometer for Measurement of Elbow Joint Motions: A Comparative Study
Abstract
Background: Universal goniometer (UG) is commonly used as a standard method to evaluate range of motion (ROM) as part of joint motions. It has some restrictions, such as involvement of both hands of the physician, leads to instability of hands and error. Nowadays smartphones usage has been increasing due to its easy application.
Objectives: The study was designed to compare the smartphone inclinometer-based app and UG in evaluation of ROM of elbow.
Materials and methods: The maximum ROM of elbow in position of flexion and pronation and supination of forearm were examined in 60 healthy volunteers with UG and smartphone. Data were analyzed using SPSS (ver. 16) software and appropriate statistical tests were applied, such as paired t-test, ICC and Bland Altman curves.
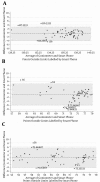
Results: The results of this study showed high reliability and validity of smartphone in regarding UG with ICC > 0.95. The highest reliability for both methods was in elbow supination and the lowest was in the elbow flexion (0.84).
Conclusions: Smartphones due to ease of access and usage for the physician and the patient, may be good alternatives for UG.
Keywords: Elbow Joint; Goniometry; Range of Motion; Smartphone.
Figures
References
-
- Ghanjal A. Comparison of permanent impairment measuring methods. Iran J Mil Med Spring. 2010;12(1):13–8.
-
- Rondinelli RD, Genovese E, Brigham C, American Medical Associaacion . Guides to the evaluation of permanent impairment. American Medical Association; 2008.
-
- Morrey BF, Sanchez-Sotelo J. The elbow and its disorders. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2009.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
