Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function
- PMID: 27626381
- PMCID: PMC5204372
- DOI: 10.1038/nature19364
Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function
Abstract
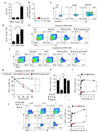
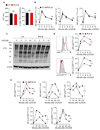
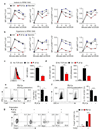
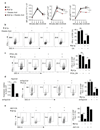
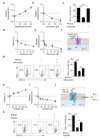
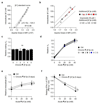
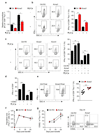
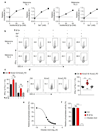
Tumours progress despite being infiltrated by tumour-specific effector T cells. Tumours contain areas of cellular necrosis, which are associated with poor survival in a variety of cancers. Here, we show that necrosis releases intracellular potassium ions into the extracellular fluid of mouse and human tumours, causing profound suppression of T cell effector function. Elevation of the extracellular potassium concentration ([K+]e) impairs T cell receptor (TCR)-driven Akt-mTOR phosphorylation and effector programmes. Potassium-mediated suppression of Akt-mTOR signalling and T cell function is dependent upon the activity of the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2A. Although the suppressive effect mediated by elevated [K+]e is independent of changes in plasma membrane potential (Vm), it requires an increase in intracellular potassium ([K+]i). Accordingly, augmenting potassium efflux in tumour-specific T cells by overexpressing the potassium channel Kv1.3 lowers [K+]i and improves effector functions in vitro and in vivo and enhances tumour clearance and survival in melanoma-bearing mice. These results uncover an ionic checkpoint that blocks T cell function in tumours and identify potential new strategies for cancer immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Immunology: Channelling potassium to fight cancer.Nature. 2016 Sep 22;537(7621):497-499. doi: 10.1038/nature19467. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27626384 No abstract available.
-
Potassium channels of T lymphocytes take center stage in the fight against cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Jan 17;5:2. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0202-5. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28105369 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

