Posterior Double Vertebral Column Resections Combined with Satellite Rod Technique to Correct Severe Congenital Angular Kyphosis
- PMID: 27627727
- PMCID: PMC6584385
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12265
Posterior Double Vertebral Column Resections Combined with Satellite Rod Technique to Correct Severe Congenital Angular Kyphosis
Abstract
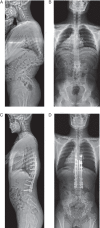
This paper presents a highly challenging technique involving posterior double vertebral column resections (VCRs) and satellite rods placement. This was a young adult case with severe angular thoracolumbar kyphosis of 101 degrees, secondary to anterior segmentation failure from T11 to L1 . There were hemivertebrae at T11 and T12 , and a wedged vertebra at L1 . He received double VCRs at T12 and T11 and instrumented fusion from T6 to L4 via a posterior only approach. Autologous grafts and a cage were placed between the bony surfaces of the osteotomy gap. Once closure of osteotomy was achieved, bilateral permanent CoCr rods were placed with addition of satellite rods. Postoperative X-ray demonstrated marked correction of kyphosis. On the 10(th) days after surgery, the patient was able to walk without assistance. In conclusion, double VCRs are effective to correct severe angular kyphosis, and addition of satellite rods may be imperative to enhance instrumentation strength and thus prevent correction loss.
Keywords: Satellite rod; Three-column osteotomy; Vertebral column resection; congenital kyphosis.
© 2016 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ, Lee SM, Chung ER, Nah KH. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2002, 27: 2374–2382. - PubMed
-
- Hamzaoglu A, Alanay A, Ozturk C, Sarier M, Karadereler S, Ganiyusufoglu K. Posterior vertebral column resection in severe spinal deformities: a total of 102 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2011, 36: E340–E344. - PubMed
-
- Lenke LG, O'Leary PT, Bridwell KH, Sides BA, Koester LA, Blanke KM. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity: minimum two‐year follow‐up of thirty‐five consecutive patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 2009, 34: 2213–2221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

