Why are acute ischemic stroke patients not receiving IV tPA? Results from a national registry
- PMID: 27629092
- PMCID: PMC5067546
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003198
Why are acute ischemic stroke patients not receiving IV tPA? Results from a national registry
Abstract
Objective: To determine patient and hospital characteristics associated with not providing IV tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to eligible patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) in clinical practice.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of patients with AIS arriving within 2 hours of onset to hospitals participating in Get With The Guidelines-Stroke without documented contraindications to IV tPA from April 2003 through December 2011, comparing those who received tPA to those who did not. Multivariable generalized estimating equation logistic regression modeling identified factors associated with not receiving tPA.
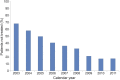
Results: Of 61,698 eligible patients with AIS presenting within 2 hours of onset (median age 73 years, 51% female, 74% non-Hispanic white, median NIH Stroke Scale score 11, interquartile range 6-18), 15,282 (25%) were not treated with tPA within 3 hours. Failure to give tPA decreased over time from 55% in 2003 to 2005 to 18% in 2010 to 2011 (p < 0.0001). After adjustment for all covariates, including stroke severity, factors associated with failure to treat included older age, female sex, nonwhite race, diabetes mellitus, prior stroke, atrial fibrillation, prosthetic heart valve, NIH Stroke Scale score <5, arrival off-hours and not via emergency medical services, longer onset-to-arrival and door-to-CT times, earlier calendar year, and arrival at rural, nonteaching, non-stroke center hospitals located in the South or Midwest.
Conclusions: Overall, about one-quarter of eligible patients with AIS presenting within 2 hours of stroke onset failed to receive tPA treatment. Thrombolysis has improved dramatically over time and is strongly associated with stroke center certification. Additionally, some groups, including older patients, milder strokes, women, and minorities, may be undertreated.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter re: Why are acute ischemic stroke patients not receiving IV tPA? Results from a national registry.Neurology. 2017 Apr 4;88(14):1383. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003802. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28373370 No abstract available.
-
Author response: Why are acute ischemic stroke patients not receiving IV tPA? Results from a national registry.Neurology. 2017 Apr 4;88(14):1383. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003801. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28373371 No abstract available.
References
-
- rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke: the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1317–1329. - PubMed
-
- Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013;44:870–947. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous