Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Genetic Disease That Involves Mucociliary Dysfunction of the Peripheral Airways
- PMID: 27630174
- PMCID: PMC5243224
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2016
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Genetic Disease That Involves Mucociliary Dysfunction of the Peripheral Airways
Abstract
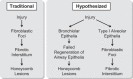
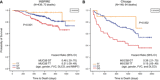
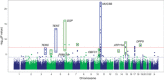
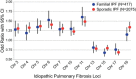
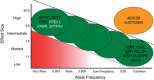
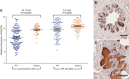
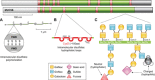
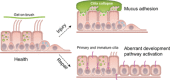
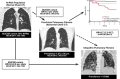
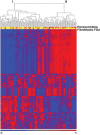
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is an incurable complex genetic disorder that is associated with sequence changes in 7 genes (MUC5B, TERT, TERC, RTEL1, PARN, SFTPC, and SFTPA2) and with variants in at least 11 novel loci. We have previously found that 1) a common gain-of-function promoter variant in MUC5B rs35705950 is the strongest risk factor (genetic and otherwise), accounting for 30-35% of the risk of developing IPF, a disease that was previously considered idiopathic; 2) the MUC5B promoter variant can potentially be used to identify individuals with preclinical pulmonary fibrosis and is predictive of radiologic progression of preclinical pulmonary fibrosis; and 3) MUC5B may be involved in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis with MUC5B message and protein expressed in bronchiolo-alveolar epithelia of IPF and the characteristic IPF honeycomb cysts. Based on these considerations, we hypothesize that excessive production of MUC5B either enhances injury due to reduced mucociliary clearance or impedes repair consequent to disruption of normal regenerative mechanisms in the distal lung. In aggregate, these novel considerations should have broad impact, resulting in specific etiologic targets, early detection of disease, and novel biologic pathways for use in the design of future intervention, prevention, and mechanistic studies of IPF.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Antonarakis SE, Chakravarti A, Cohen JC, Hardy J. Mendelian disorders and multifactorial traits: the big divide or one for all? Nat Rev Genet 11: 380–384, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Araki T, Putman RK, Hatabu H, Gao W, Dupuis J, Latourelle JC, Nishino M, Zazueta OE, Kurugol S, Ross JC, Estepar RS, Schwartz DA, Rosas IO, Washko GR, O'Connor GT, Hunninghake GM. Development and progression of interstitial lung abnormalities in the Framingham Heart Study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. In press. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armanios MY, Chen JJ, Cogan JD, Alder JK, Ingersoll RG, Markin C, Lawson WE, Xie M, Vulto I, Phillips JA 3rd, Lansdorp PM, Greider CW, Loyd JE. Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 356: 1317–1326, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Baek HA, Kim do S, Park HS, Jang KY, Kang MJ, Lee DG, Moon WS, Chae HJ, Chung MJ. Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in myofibroblastic differentiation of lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 46: 731–739, 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL092870/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL120770/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 HL123442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES023384/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX001534/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL097163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 ES025476/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130938/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL120770/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 HL123442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

