Intrahepatic Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Chronic HBV Infection Subjects: Asymptomatic Carriers, Active Chronic Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 27630720
- PMCID: PMC5010883
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.34432
Intrahepatic Toll-Like Receptor 3 in Chronic HBV Infection Subjects: Asymptomatic Carriers, Active Chronic Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The entire disease spectrum of chronic HBV infection (CHB) includes asymptomatic carriers (AC), active chronic hepatitis (ACH), cirrhosis (Cir), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Previous study have demonstrated that the costimulation profiles from the livers of patients influenced immune responses and played various immunological roles in AC, ACH, Cir, and HCC. In addition, activation of TLR3 signaling in the liver may contribute to HBV clearance, although some HBV components are able to block TLR3 signaling and counteract HBV clearance through positive or negative feedback loops. Previous clinical studies have demonstrated that different TLR3 expressions are present in ACH patients, but no studies investigated the expression of TLR3 proteins in the livers of patients with AC, Cir, or HCC.
Objectives: This study investigated intrahepatic TLR3 expression throughout the entire disease spectrum of CHB patients and assessed the interrelations between TLR3 and costimulation proteins.
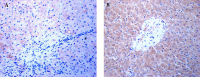
Patients and methods: Patients with ACH, Cir, HCC, and AC and healthy donors (HD) were recruited. TLR3 expression in the livers of patients were investigated using western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry. Correlations between TLR3 and costimulation proteins, including CD80, CD86, CD83, CD28, CTLA-4, CD40, and ICAM-1, were assessed.
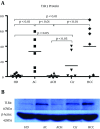
Results: The TLR3 protein in the ACH group tended toward reduction although the P Value of the comparison between the ACH group and HD group was not statistically significant. The TLR3 levels in the HCC, AC, and Cir groups were higher than those in the HD and ACH groups. TLR3 was not interrelated with all costimulation proteins in the DCs and T cells in all five groups. No group presented any interrelation between TLR3 and CD40, except the AC group.
Conclusions: The AC, HCC, and Cir patients displayed increased levels of the intrahepatic TLR3 protein compared to the HD and AC patients. Both activation of TLR3/INF-β signaling and inhibition of TLR3/INF-β signaling by HBV components influenced TLR3 expression in the AC, ACH, Cir, and HCC subjects. However, TLR3 signaling did not influence the expression of costimulatory protein in the ACH, Cir, or HCC patients. TLR3/ IFN-β signaling did influence immune responses in the livers of CHB patients.
Keywords: Chronic Hepatitis B Infection; Costimulatory Molecule; Intrahepatic Immunopathophysiology; Toll-Like Receptors; Toll-Like Receptors 3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of costimulation on intrahepatic immunopathogenesis in patients with chronic HBV infection.Inflamm Res. 2014 Mar;63(3):217-29. doi: 10.1007/s00011-013-0691-3. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Inflamm Res. 2014. PMID: 24337678 Free PMC article.
-
Association of mRNA expression of toll-like receptor 2 and 3 with hepatitis B viral load in chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.J Med Virol. 2017 Jun;89(6):1008-1014. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24719. Epub 2017 Jan 10. J Med Virol. 2017. PMID: 27769109
-
Analysis of Notch and TGF-β Signaling Expression in Different Stages of Disease Progression During Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct 4;3(10):e23. doi: 10.1038/ctg.2012.17. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23238065 Free PMC article.
-
Risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in the course of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and the protective effect of therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogues.World J Hepatol. 2015 May 18;7(8):1064-73. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i8.1064. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26052395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What can we learn from hepatitis B virus clinical cohorts?Liver Int. 2015 Jan;35 Suppl 1:91-9. doi: 10.1111/liv.12716. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25529093 Review.
Cited by
-
Chinese Patent Medicine Liuweiwuling Tablet had Potent Inhibitory Effects on Both Wild-Type and Entecavir-Resistant Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) in vitro and Effectively Suppressed HBV Replication in Mouse Model.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 27;12:756975. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.756975. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34776974 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms during Hepatitis B Infection and the Effects of the Virus Variability.Viruses. 2021 Jun 18;13(6):1167. doi: 10.3390/v13061167. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34207116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Shenlingyigan decoction on inflammatory factors related to liver injury regulated by TLR3 signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 23;10(3):e24611. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24611. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38322849 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of immune control in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Clinical implications on immunity with interferon-α treatment and retreatment.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Oct 28;28(40):5784-5800. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i40.5784. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36353205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of increased expression of RACO-1 in patients with hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Feb 15;13:191-200. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S125331. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28243109 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
