A Role of Ginseng and Its Constituents in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders
- PMID: 27630732
- PMCID: PMC5007341
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/2614742
A Role of Ginseng and Its Constituents in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
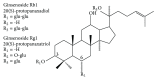
Ginseng, a perennial plant belonging to the Panax genus of the Araliaceae family, has been used in China, Korea, and Japan as a traditional herbal medicine for thousands of years. Ginseng is recorded to have exhibited a wide variety of beneficial pharmacological effects and has become a popular and worldwide known health supplement and drug. The protective effects of ginseng on central nervous system are discussed in this review. Ginseng species and ginsenosides and their intestinal metabolism and bioavailability are concisely introduced. The molecular mechanisms of the effects of ginseng on central nervous system, mainly focused on the neuroprotection properties of ginseng, memory, and learning enhanced properties, and the effects on neurodegenerative disorders are presented. Thus, ginseng and its constituents are of potential merits in the treatment of cerebral disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Lu G.-H., Zhou Q., Sun S.-Q., Leung K. S.-Y., Zhang H., Zhao Z.-Z. Differentiation of Asian ginseng, American ginseng and Notoginseng by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy combined with two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Molecular Structure. 2008;883-884(1–3):91–98. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.12.008. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

