ePGA: A Web-Based Information System for Translational Pharmacogenomics
- PMID: 27631363
- PMCID: PMC5025168
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162801
ePGA: A Web-Based Information System for Translational Pharmacogenomics
Abstract
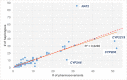
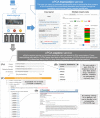
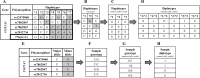
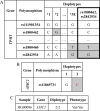
One of the challenges that arise from the advent of personal genomics services is to efficiently couple individual data with state of the art Pharmacogenomics (PGx) knowledge. Existing services are limited to either providing static views of PGx variants or applying a simplistic match between individual genotypes and existing PGx variants. Moreover, there is a considerable amount of haplotype variation associated with drug metabolism that is currently insufficiently addressed. Here, we present a web-based electronic Pharmacogenomics Assistant (ePGA; http://www.epga.gr/) that provides personalized genotype-to-phenotype translation, linked to state of the art clinical guidelines. ePGA's translation service matches individual genotype-profiles with PGx gene haplotypes and infers the corresponding diplotype and phenotype profiles, accompanied with summary statistics. Additional features include i) the ability to customize translation based on subsets of variants of clinical interest, and ii) to update the knowledge base with novel PGx findings. We demonstrate ePGA's functionality on genetic variation data from the 1000 Genomes Project.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Sebelius K, Frieden TR, Sondik EJ. Health, United States, 2009 with Special Feature on Medical Technology. National Center for Health Statistics. 2009. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

