Effectiveness of Telephone-Based Health Coaching for Patients with Chronic Conditions: A Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 27632360
- PMCID: PMC5025178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161269
Effectiveness of Telephone-Based Health Coaching for Patients with Chronic Conditions: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Chronic diseases, like diabetes mellitus, heart disease and cancer are leading causes of death and disability. These conditions are at least partially preventable or modifiable, e.g. by enhancing patients' self-management. We aimed to examine the effectiveness of telephone-based health coaching (TBHC) in chronically ill patients.
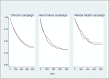
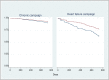
Methods and findings: This prospective, pragmatic randomized controlled trial compares an intervention group (IG) of participants in TBHC to a control group (CG) without TBHC. Endpoints were assessed two years after enrolment. Three different groups of insurees with 1) multiple conditions (chronic campaign), 2) heart failure (heart failure campaign), or 3) chronic mental illness conditions (mental health campaign) were targeted. The telephone coaching included evidence-based information and was based on the concepts of motivational interviewing, shared decision-making, and collaborative goal setting. Patients received an average of 12.9 calls. Primary outcome was time from enrolment until hospital readmission within a two-year follow-up period. Secondary outcomes comprised the probability of hospital readmission, number of daily defined medication doses (DDD), frequency and duration of inability to work, and mortality within two years. All outcomes were collected from routine data provided by the statutory health insurance. As informed consent was obtained after randomization, propensity score matching (PSM) was used to minimize selection bias introduced by decliners. For the analysis of hospital readmission and mortality, we calculated Kaplan-Meier curves and estimated hazard ratios (HR). Probability of hospital readmission and probability of death were analysed by calculating odds ratios (OR). Quantity of health service use and inability to work were analysed by linear random effects regression models. PSM resulted in patient samples of 5,309 (IG: 2,713; CG: 2,596) in the chronic campaign, of 660 (IG: 338; CG: 322) in the heart failure campaign, and of 239 (IG: 101; KG: 138) in the mental health campaign. In none of the three campaigns, there were significant differences between IG and CG in time until hospital readmission. In the chronic campaign, the probability of hospital readmission was higher in the IG than in the CG (OR = 1.13; p = 0.045); no significant differences could be found for the other two campaigns. In the heart failure campaign, the IG showed a significantly reduced number of hospital admissions (-0.41; p = 0.012), although the corresponding reduction in the number of hospital days was not significant. In the chronic campaign, the IG showed significantly increased number of DDDs. Most striking, there were significant differences in mortality between IG and CG in the chronic campaign (OR = 0.64; p = 0.005) as well as in the heart failure campaign (OR = 0.44; p = 0.001).
Conclusions: While TBHC seems to reduce hospitalization only in specific patient groups, it may reduce mortality in patients with chronic somatic conditions. Further research should examine intervention effects in various subgroups of patients, for example for different diagnostic groups within the chronic campaign, or duration of coaching.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register DRKS00000584.
Conflict of interest statement
Two of the co-authors (LH, ESS) are employed by the KKH. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures

References
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–223. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095–128. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bloom DE, Cafiero ET, Jané-Llopis E, Abrahams-Gessel S, Bloom LR, Fathima S., Feigl AB, et al. The global economic burden of non-communicable diseases. Geneva: World Economic Forum, 2011.
-
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Chronic conditions among Medicare beneficiaries, chartbook, 2012 edition 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

