A LC-MS/MS Method for Quantifying Adenosine, Guanosine and Inosine Nucleotides in Human Cells
- PMID: 27633886
- PMCID: PMC5177511
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-016-2040-z
A LC-MS/MS Method for Quantifying Adenosine, Guanosine and Inosine Nucleotides in Human Cells
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and validate a method for the simultaneous measurement of adenosine, guanosine, and inosine derived from mono (MP) and triphosphate (TP) forms in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), red blood cells (RBCs) and dried blood spots (DBS).
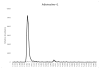
Methods: Solid phase extraction of cell lysates followed by dephosphorylation to molar equivalent nucleoside and LC-MS/MS quantification.
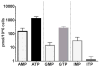
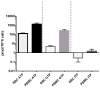
Results: The assay was linear for each of the three quantification ranges: 10-2000, 1.0-200 and 0.25-50 pmol/sample for adenosine, guanosine, and inosine, respectively. Intraassay (n = 6) and interassay (n = 18) precision (%CV) were within 1.7 to 16% while accuracy (%deviation) was within -11.5 to 14.7% for all three analytes. Nucleotide monophosphates were less concentrated than triphosphates (except for inosine) and levels in PBMCs were higher than RBCs for all three nucleotides (10, 55, and 5.6 fold for ATP, GTP and ITP, respectively). DBS samples had an average (SD) of -26% (22.6%) lower TP and 184% (173%) higher MP levels compared to paired RBC lysates, suggesting hydrolysis of the TP in DBS.
Conclusion: This method was accurate and precise for physiologically relevant concentrations of adenosine, guanosine and inosine nucleotides in mono- and triphosphate forms, providing a bioanalytical tool for quantitation of nucleotides for clinical studies.
Keywords: LC-MS/MS; analytical method; dried blood spots; intracellular quantification; purine nucleotides.
Figures


References
-
- Scheele KW. Examen chemicum calculi urinarii. Opuscula. 1776;73(2)
-
- Nyhan WL. Disorders of purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Mol Genet Metab. 2005;86(1–2):25–33. - PubMed
-
- Edwards NL, Fox IH. Disorders associated with purine and pyrimidine metabolism. Spec Top Endocrinol Metab. 1984;6:95–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

