Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Gli-1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 27634907
- PMCID: PMC5356614
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12011
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Gli-1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Glioma associated oncogene-1 (Gli-1) is considered as a strong positive activator of downstream target genes of hedgehog signal pathway in mammalians. However, its diagnostic and prognostic value in gastric cancer remains unclear and controversial. Therefore, a quantitative meta-analysis was conducted to determine the clinical value of Gli-1 in gastric cancer patients. Twelve eligible articles with 886 gastric cancer patients were included in this meta-analysis. The relationship between Gli-1 expression in gastric cancer patients and clinicopathological features and 5-year overall survival (OS) was evaluated using pooled odds ratios (ORs) and hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The meta-analysis showed that the upregulated Gli-1 was associated with sample type (gastric cancer tissues) (OR 10.31, 95%CI 7.14-14.88; P = 0.000), differentiation type (OR 3.76, 95%CI 2.55-5.53; P = 0.000), depth of invasion (OR 8.17, 95%CI 3.60-18.55; P = 0.000), lymph node metastasis (OR 3.97, 95%CI 2.73-5.78; P = 0.000) and high TNM stage (OR 3.65, 95%CI 1.89-7.04; P = 0.000). Three studies including 316 patients were assessed for the correlation between Gli-1 and 5-year OS, which indicated that positive Gli-1 expression was associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients (HR 2.14, 95%CI 1.35-3.40; P = 0.001). Little publication bias was identified by funnel plots and Egger's tests. The sensitivity analysis indicated that no study substantially influenced pooled OR/HR. Taken together, Gli-1 is a credible indicator for highly aggressive tumor with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Keywords: Gli-1; gastric cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
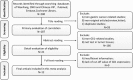




References
-
- Parkin DM. Global cancer statistics in the year 2000. Lancet Oncol. 2001;2:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Kundu JK, Surh YJ. Cancer chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of resveratrol: mechanistic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2008;269:243–261. - PubMed
-
- Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Høiby T, Stefansson I, Haugen H, Sandal T, Collett K, Li S, McCormack E, Gjertsen BT, Micklem DR, Akslen LA, Glackin C, et al. Axl is an essential epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:1124–1129. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

