Regulation of Dopamine Uptake by Vasoactive Peptides in the Kidney
- PMID: 27635280
- PMCID: PMC5011208
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6302376
Regulation of Dopamine Uptake by Vasoactive Peptides in the Kidney
Abstract
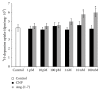
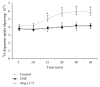
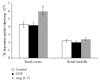
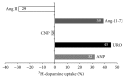
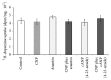
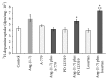
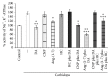
Considering the key role of renal dopamine in tubular sodium handling, we hypothesized that c-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) and Ang-(1-7) may regulate renal dopamine availability in tubular cells, contributing to Na(+), K(+)-ATPase inhibition. Present results show that CNP did not affect either (3)H-dopamine uptake in renal tissue or Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity; meanwhile, Ang-(1-7) was able to increase (3)H-dopamine uptake and decreased Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity in renal cortex. Ang-(1-7) and dopamine together decreased further Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity showing an additive effect on the sodium pump. In addition, hydrocortisone reversed Ang-(1-7)-dopamine overinhibition on the enzyme, suggesting that this inhibition is closely related to Ang-(1-7) stimulation on renal dopamine uptake. Both anantin and cANP (4-23-amide) did not modify CNP effects on (3)H-dopamine uptake by tubular cells. The Mas receptor antagonist, A-779, blocked the increase elicited by Ang-(1-7) on (3)H-dopamine uptake. The stimulatory uptake induced by Ang-(1-7) was even more pronounced in the presence of losartan, suggesting an inhibitory effect of Ang-(1-7) on AT1 receptors on (3)H-dopamine uptake. By increasing dopamine bioavailability in tubular cells, Ang-(1-7) enhances Na(+), K(+)-ATPase activity inhibition, contributing to its natriuretic and diuretic effects.
Figures

References
-
- Tsuchida H., Imai G., Shima Y., Satoh T., Owada S. Mechanism of sodium load-induced hypertension in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus model rats: defective dopaminergic system to inhibit Na-K-ATPase activity in renal epithelial cells. Hypertension Research. 2001;24(2):127–135. doi: 10.1291/hypres.24.127. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zeng C., Armando I., Luo Y., Eisner G. M., Felder R. A., Jose P. A. Dysregulation of dopamine-dependent mechanisms as a determinant of hypertension: studies in dopamine receptor knockout mice. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2008;294(2):H551–H569. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01036.2007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bełtowski J., Wójcicka G. Regulation of renal tubular sodium transport by cardiac natriuretic peptides: two decades of research. Medical Science Monitor. 2002;8(2):RA39–RA52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

