Colorimetric Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Identification of Chemical Weapons and Explosives
- PMID: 27636675
- PMCID: PMC5351797
- DOI: 10.1080/10408347.2016.1233805
Colorimetric Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Identification of Chemical Weapons and Explosives
Abstract
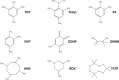
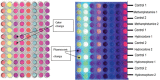
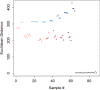
There is a significant demand for devices that can rapidly detect chemical-biological-explosive (CBE) threats on-site and allow for immediate responders to mitigate spread, risk, and loss. The key to an effective reconnaissance mission is a unified detection technology that analyzes potential threats in real time. In addition to reviewing the current state of the art in the field, this review illustrates the practicality of colorimetric arrays composed of sensors that change colors in the presence of analytes. This review also describes an outlook toward future technologies, and describes how they could possibly be used in areas such as war zones to detect and identify hazardous substances.
Keywords: Colorimetric arrays; chemical detection; explosives; field testing; handheld devices; principal component analysis; red green blue (RGB) analysis; smartphone technology.
Figures

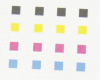


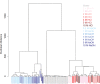
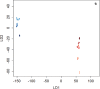




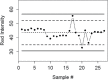
References
-
- Afkhami A.; Sarlak N.. A Novel Cyanide Sensing Phase Based on Immobilization of Methyl Violet on A Triacetylcellulose Membrane. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2007, , 437–441. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2006.06.012 - DOI
-
- Amani M.; Chu Y.; Waterman K. L.; Hurley C. M.; Platek M. J.; Gregory O. J.. Detection of Triacetone Triperoxide (TATP) Using a Thermodynamic Based Gas Sensor. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2012, , 7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2011.11.019 - DOI
-
- Arrayit Corporation [WWW Document]. http://shop.arrayit.com/ Accessed on June.17.16, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
