Down-regulated resistin level in consequence of decreased neutrophil counts in untreated Grave's disease
- PMID: 27637079
- PMCID: PMC5346669
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12019
Down-regulated resistin level in consequence of decreased neutrophil counts in untreated Grave's disease
Abstract
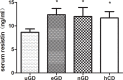
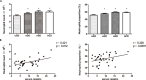
Resistin, belongs to cysteine-rich secretory protein, is mainly produced by circulating leukocytes, such as neutrophils monocytes and macrophages in humans. To date, few but controversial studies have reported about resistin concentrations in hyperthyroid patients, especially in Graves' disease (GD). We undertaked a controlled, prospective study to explore the serum resistin concentration in GD patients before and after -MMI treatment. In addition, we also investigated the main influencing factor on serum resistin level and discuessed the potential role of serum resistin plays in GD patients. 39 untreated GD (uGD) patients, including 8 males and 31 females, were enrolled in our investigation. All of these patients were prescribed with MMI treatment, in addition to 25 healthy controls. Anthropometric parameters and hormone assessment were measured. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect serum resistin concentration in different stages of GD patients. Furthermore, neutrophil cell line NB4 with or without T3 treatment to detect the effect of thyroid hormones on resistin expression. The serum resistin level and neutrophil counts in untreated GD patients were significantly declined. And all of these parameters were recovered to normal after MMI treatment in ethyroid GD (eGD) and TRAb-negative conversion (nGD) patients. Resistin concentration exhibited a negative correlation with FT3 and FT4, but a positive correlation with absolute number of neutrophiles in uGD patients, whereas did not correlate with thyroid autoimmune antibodies and BMI. Neutrophile cell line, NB4, produced decreased expression of resistin when stimulated with T3. Our study showed a decrease of serum resistin level in GD patients and we suggested that the serum resistin might primarily secreted from circulating neutrophils and down-regulated by excessive thyroid hormones in GD patients.
Keywords: Graves’ disease; T3; neutrophils; resistin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Significance of thyroid blood flow as a predictor of methimazole sensitivity in untreated hyperthyroid patients with Graves' disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2007 Sep;61(8):472-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2007.02.002. Epub 2007 Mar 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17420111
-
Serum concentrations of adiponectin and resistin in hyperthyroid Graves' disease patients.J Endocrinol Invest. 2008 Sep;31(9):745-9. doi: 10.1007/BF03349251. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008. PMID: 18997483
-
Decreased serum level of IL-7 in patients with active Graves' disease.Cytokine. 2015 Oct;75(2):373-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.04.020. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26113403
-
Elevated serum IL-16 and RANTES levels in patients with autoimmune thyroid diseases and modulation by methimazole therapy.Horm Metab Res. 2012 Jun;44(6):482-7. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1308973. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Horm Metab Res. 2012. PMID: 22473756 Clinical Trial.
-
Increase of interferon-gamma-inducible CXC chemokine CXCL10 serum levels in patients with active Graves' disease, and modulation by methimazole therapy.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006 Feb;64(2):189-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02447.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. PMID: 16430719
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Thyroid Dysfunction and Ovarian Cancer.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 14;15(6):870. doi: 10.3390/biom15060870. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmune thyroid disease disrupts immune homeostasis in the endometrium of unexplained infertility women-a single-cell RNA transcriptome study during the implantation window.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 12;14:1185147. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1185147. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37501789 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Resistin Gene Polymorphisms and Atopic Dermatitis.Biomolecules. 2018 Mar 27;8(2):17. doi: 10.3390/biom8020017. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 29584687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM, Patel HR, Ahima RS, Lazar MA. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature. 2001;409:307–312. - PubMed
-
- Kim KH, Lee K, Moon YS, Sul HS. A cysteine-rich adipose tissue-specific secretory factor inhibits adipocyte differentiation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2001;276:11252–11256. - PubMed
-
- Rajala MW, Qi Y, Patel HR, Takahashi N, Banerjee R, Pajvani UB, Sinha MK, Gingerich RL, Scherer PE, Ahima RS. Regulation of resistin expression and circulating levels in obesity, diabetes, and fasting. Diabetes. 2004;53:1671–1679. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee RR, Rangwala SM, Shapiro JS, Rich AS, Rhoades B, Qi Y, Wang J, Rajala MW, Pocai A, Scherer PE, Steppan CM, Ahima RS, Obici S, et al. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science (New York, NY) 2004;303:1195–1198. - PubMed
-
- Li FP, He J, Li ZZ, Luo ZF, Yan L, Li Y. Effects of resistin expression on glucose metabolism and hepatic insulin resistance. Endocrine. 2009;35:243–251. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

