Incentive and Reminder Strategies to Improve Response Rate for Internet-Based Physician Surveys: A Randomized Experiment
- PMID: 27637296
- PMCID: PMC5045523
- DOI: 10.2196/jmir.6318
Incentive and Reminder Strategies to Improve Response Rate for Internet-Based Physician Surveys: A Randomized Experiment
Abstract
Background: Most research on how to enhance response rates in physician surveys has been done using paper surveys. Uncertainties remain regarding how to enhance response rates in Internet-based surveys.
Objective: To evaluate the impact of a low-cost nonmonetary incentive and paper mail reminders (formal letter and postcard) on response rates in Internet-based physician surveys.
Methods: We executed a factorial-design randomized experiment while conducting a nationally representative Internet-based physician survey. We invited 3966 physicians (randomly selected from a commercial database of all licensed US physicians) via email to complete an Internet-based survey. We used 2 randomly assigned email messages: one message offered a book upon survey completion, whereas the other did not mention the book but was otherwise identical. All nonrespondents received several email reminders. Some physicians were further assigned at random to receive 1 reminder via paper mail (either a postcard or a letter) or no paper reminder. The primary outcome of this study was the survey response rate.
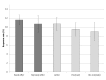
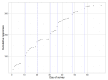
Results: Of the 3966 physicians who were invited, 451 (11.4%) responded to at least one survey question and 336 (8.5%) completed the entire survey. Of those who were offered a book, 345/2973 (11.6%) responded compared with 106/993 (10.7%) who were not offered a book (odds ratio 1.10, 95% CI 0.87-1.38, P=.42). Regarding the paper mail reminder, 168/1572 (10.7%) letter recipients, 148/1561 (9.5%) postcard recipients, and 69/767 (9.0%) email-only recipients responded (P=.35). The response rate for those receiving letters or postcards was similar (odds ratio 1.14, 95% CI 0.91-1.44, P=.26).
Conclusions: Offering a modest nonmonetary incentive and sending a paper reminder did not improve survey response rate. Further research on how to enhance response rates in Internet-based physician surveys is needed.
Keywords: questionnaire design; survey methods; surveys and questionnaires.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Asch DA, Jedrziewski MK, Christakis NA. Response rates to mail surveys published in medical journals. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997 Oct;50(10):1129–36.S0895-4356(97)00126-1 - PubMed
-
- Asch S, Connor SE, Hamilton EG, Fox SA. Problems in recruiting community-based physicians for health services research. J Gen Intern Med. 2000 Aug;15(8):591–9. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pub... jgi02329 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davern M. Nonresponse rates are a problematic indicator of nonresponse bias in survey research. Health Serv Res. 2013 Jun;48(3):905–12. doi: 10.1111/1475-6773.12070. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/23656501 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

