Mutant p53 Together with TGFβ Signaling Influence Organ-Specific Hematogenous Colonization Patterns of Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 27637888
- PMCID: PMC5354987
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1615
Mutant p53 Together with TGFβ Signaling Influence Organ-Specific Hematogenous Colonization Patterns of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
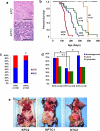
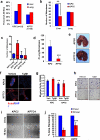
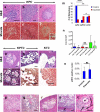
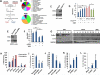
Purpose: TP53 and the TGFβ pathway are major mediators of pancreatic cancer metastasis. The mechanisms by which they cause hematogenous metastasis have not been fully explored.Experimental Design:KPC (LSL-KRASG12D/+;LSL-Trp53R172H/+; Ptf1aCre/+) mice were generated, and the frequency and morphology of organ-specific hematogenous metastases compared with that seen in KPTC and KTC littermates (Tgfbr2+/-). Key findings were validated in primary cells from each genotype and samples of human pancreatic cancer liver metastases.Results: The frequency of hematogenous metastasis in KPTC mice was significantly lower than for KPC mice (41% vs. 68%, P < 0.05), largely due to a reduction in liver metastases. No differences were found between KPC and KPTC lung metastases, whereas liver metastases in KPTC mice showed a profound extravasation deficiency characterized by sinusoidal growth and lack of desmoplastic stroma. Analogous findings were confirmed in liver samples from patients indicating their clinical relevance. Portal vein colonization as a direct mode of access to the liver was observed in both mice and humans. Secretome analyses of KPC cells revealed an abundance of secreted prometastatic mediators including Col6A1 and Lcn2 that promoted early steps of metastatic colonization. These mediators were overexpressed in primary tumors but not metastases, suggesting that the ability to colonize is, in part, developed within the primary site, a phenomenon we refer to as the "Cinderella effect."Conclusions: These findings establish a novel paradigm for understanding pancreatic cancer metastasis and the observed clinical latencies of liver versus lung metastases specifically. Clin Cancer Res; 23(6); 1607-20. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


References
-
- Stathis A, Moore MJ. Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010;7:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. American Association for Cancer Research. 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
-
- Yachida S, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA. The pathology and genetics of metastatic pancreatic cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:413–22. - PubMed
-
- Hingorani SR, Wang L, Multani AS, Combs C, Deramaudt TB, Hruban RH, et al. Trp53R172H and KrasG12D cooperate to promote chromosomal instability and widely metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:469–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

