FACIN, a Double-Edged Sword of the Emerging Periodontal Pathogen Filifactor alocis: A Metabolic Enzyme Moonlighting as a Complement Inhibitor
- PMID: 27638863
- PMCID: PMC5101141
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600739
FACIN, a Double-Edged Sword of the Emerging Periodontal Pathogen Filifactor alocis: A Metabolic Enzyme Moonlighting as a Complement Inhibitor
Abstract
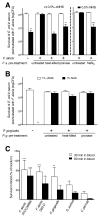
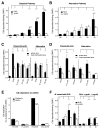
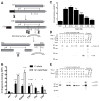
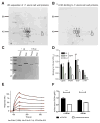
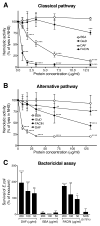
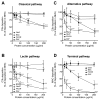
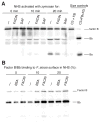
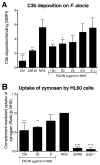
Periodontal disease is one of the most common inflammatory infectious diseases worldwide and it is associated with other syndromes, such as cardiovascular disease or rheumatoid arthritis. Recent advances in sequencing allowed for identification of novel periodontopathogens such as Gram-positive Filifactor alocis, but its virulence mechanisms remain largely unknown. We confirmed that F. alocis is a prevalent species in periodontitis patients, and we also observed strong correlation of this bacterium with clinical parameters, highlighting its role in the pathogenesis of the disease. Further, we found that preincubation of human serum with F. alocis resulted in abolished bactericidal activity and that F. alocis was surviving readily in full blood. We demonstrated that one of the key contributors to F. alocis complement resistance is a unique protein, FACIN (F. alocis complement inhibitor), which binds to C3, resulting in suppression of all complement pathways. Interestingly, FACIN is a nonclassical cell surface protein, a cytosolic enzyme acetylornithine transaminase, for which we now identified a moonlighting function. FACIN binds to C3 alone, but more importantly it also captures activated complement factor 3 within the complex with factor B, thereby locking in the convertase in an inactive state. Because of the indispensable role of alternative pathway convertase in amplifying complement cascades, its inhibition by FACIN results in a very potent downregulation of activated complement factor 3 opsonization on the pathogen surface, accompanied by reduction of downstream C5 cleavage.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Suvan J, D’Aiuto F, Moles DR, Petrie A, Donos N. Association between overweight/obesity and periodontitis in adults. A systematic review. Obes Rev. 12:e381–404. - PubMed
-
- Tonetti MS. Periodontitis and risk for atherosclerosis: an update on intervention trials. J Clin Periodontol. 2009;36(Suppl 10):15–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

