Existence of Neural Crest-Derived Progenitor Cells in Normal and Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy Corneal Endothelium
- PMID: 27639969
- PMCID: PMC5222986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.06.011
Existence of Neural Crest-Derived Progenitor Cells in Normal and Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy Corneal Endothelium
Abstract
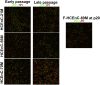
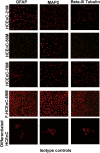
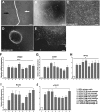
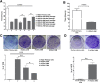
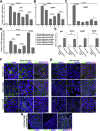
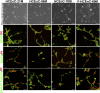
Human corneal endothelial cells are derived from neural crest and because of postmitotic arrest lack competence to repair cell loss from trauma, aging, and degenerative disorders such as Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy (FECD). Herein, we identified a rapidly proliferating subpopulation of cells from the corneal endothelium of adult normal and FECD donors that exhibited features of neural crest-derived progenitor (NCDP) cells by showing absence of senescence with passaging, propensity to form spheres, and increased colony forming efficacy compared with the primary cells. The collective expression of stem cell-related genes SOX2, OCT4, LGR5, TP63 (p63), as well as neural crest marker genes PSIP1 (p75(NTR)), PAX3, SOX9, AP2B1 (AP-2β), and NES, generated a phenotypic footprint of endothelial NCDPs. NCDPs displayed multipotency by differentiating into microtubule-associated protein 2, β-III tubulin, and glial fibrillary acidic protein positive neurons and into p75(NTR)-positive human corneal endothelial cells that exhibited transendothelial resistance of functional endothelium. In conclusion, we found that mitotically incompetent ocular tissue cells contain adult NCDPs that exhibit a profile of transcription factors regulating multipotency and neural crest progenitor characteristics. Identification of normal NCDPs in FECD-affected endothelium holds promise for potential autologous cell therapies.
Copyright © 2016 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Joyce N.C. Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2003;22:359–389. - PubMed
-
- Bourne W.M. Biology of the corneal endothelium in health and disease. Eye (Lond) 2003;17:912–918. - PubMed
-
- Dobbins K.R., Price F.W., Jr., Whitson W.E. Trends in the indications for penetrating keratoplasty in the midwestern United States. Cornea. 2000;19:813–816. - PubMed
-
- Ghosheh F.R., Cremona F.A., Rapuano C.J., Cohen E.J., Ayres B.D., Hammersmith K.M., Raber I.M., Laibson P.R. Trends in penetrating keratoplasty in the United States 1980-2005. Int Ophthalmol. 2008;28:147–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

