The DEAD-Box Protein Dhh1p Couples mRNA Decay and Translation by Monitoring Codon Optimality
- PMID: 27641505
- PMCID: PMC5635654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.053
The DEAD-Box Protein Dhh1p Couples mRNA Decay and Translation by Monitoring Codon Optimality
Abstract
A major determinant of mRNA half-life is the codon-dependent rate of translational elongation. How the processes of translational elongation and mRNA decay communicate is unclear. Here, we establish that the DEAD-box protein Dhh1p is a sensor of codon optimality that targets an mRNA for decay. First, we find mRNAs whose translation elongation rate is slowed by inclusion of non-optimal codons are specifically degraded in a Dhh1p-dependent manner. Biochemical experiments show Dhh1p is preferentially associated with mRNAs with suboptimal codon choice. We find these effects on mRNA decay are sensitive to the number of slow-moving ribosomes on an mRNA. Moreover, we find Dhh1p overexpression leads to the accumulation of ribosomes specifically on mRNAs (and even codons) of low codon optimality. Lastly, Dhh1p physically interacts with ribosomes in vivo. Together, these data argue that Dhh1p is a sensor for ribosome speed, targeting an mRNA for repression and subsequent decay.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
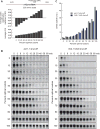




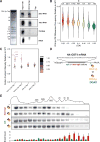
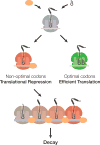
Comment in
-
RNA decay: Dhh1p condemns mRNAs with non-optimal codons to decay.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Nov;17(11):675. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.136. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27677858 No abstract available.
-
Codon optimality and mRNA decay.Cell Res. 2016 Dec;26(12):1269-1270. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.127. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27811910 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Human DDX6 regulates translation and decay of inefficiently translated mRNAs.Elife. 2024 Jul 11;13:RP92426. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92426. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38989862 Free PMC article.
-
When mRNA translation meets decay.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Apr 15;45(2):339-351. doi: 10.1042/BST20160243. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28408474 Review.
-
The DEAD box helicase, Dhh1p, functions in mRNA decapping and interacts with both the decapping and deadenylase complexes.RNA. 2001 Dec;7(12):1717-27. doi: 10.1017/s135583820101994x. RNA. 2001. PMID: 11780629 Free PMC article.
-
Codon optimality-mediated mRNA degradation: Linking translational elongation to mRNA stability.Mol Cell. 2022 Apr 21;82(8):1467-1476. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.032. Mol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35452615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA decay: Dhh1p condemns mRNAs with non-optimal codons to decay.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Nov;17(11):675. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.136. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27677858 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Decoupling the impact of microRNAs on translational repression versus RNA degradation in embryonic stem cells.Elife. 2018 Jul 25;7:e38014. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38014. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30044225 Free PMC article.
-
Genes for highly abundant proteins in Escherichia coli avoid 5' codons that promote ribosomal initiation.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Oct 25;19(10):e1011581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011581. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37878567 Free PMC article.
-
Global Profiling of Cellular Substrates of Human Dcp2.Biochemistry. 2020 Nov 3;59(43):4176-4188. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00069. Epub 2020 May 14. Biochemistry. 2020. PMID: 32365300 Free PMC article.
-
GCN2-Like Kinase Modulates Stress Granule Formation During Nutritional Stress in Trypanosoma cruzi.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Apr 16;10:149. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00149. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32373547 Free PMC article.
-
Synonymous nucleotide modification of the KCNH2 gene affects both mRNA characteristics and translation of the encoded hERG ion channel.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 3;293(31):12120-12136. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.001805. Epub 2018 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29907571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braat AK, Yan N, Arn E, Harrison D, Macdonald PM. Localization-dependent oskar protein accumulation; control after the initiation of translation. Dev Cell. 2004;7:125–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

