Urinary Excretion of the β-Adrenergic Feed Additives Ractopamine and Zilpaterol in Breast and Lung Cancer Patients
- PMID: 27641640
- PMCID: PMC5510757
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02723
Urinary Excretion of the β-Adrenergic Feed Additives Ractopamine and Zilpaterol in Breast and Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
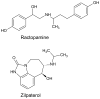
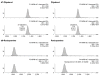
β2-Adrenergic agonists (β-agonists) have been legally used in the U.S. for almost two decades to increase lean muscle mass in meat animals. Despite a cardiotoxic effect after high-dose exposure, there has been limited research on human β-agonist exposures related to meat consumption. We quantified urinary concentrations of ractopamine and zilpaterol, two FDA-approved β-agonist feed additives, and examined the extent to which the concentrations were associated with estimated usual meat intake levels. Overnight urine samples from 324 newly diagnosed breast cancer patients and spot urine samples from 46 lung cancer patients at the time of diagnosis, prior to treatment, were collected during 2006-2010 and 2014-2015, respectively. Urinary ractopamine and zilpaterol concentrations were measured by LC-MS/MS. Ractopamine and zilpaterol, respectively, were detected in 8.1% and 3.0% of the urine samples collected (n = 370). Only 1.1% (n = 4) of the urine samples had zilpaterol concentrations above the limit of quantification, with the mean value of 0.07 ng/mL in urine. The presence of detectable ractopamine and zilpaterol levels were not associated with meat consumption estimated from a food frequency questionnaire, including total meat (P = 0.13 and 0.74, respectively), total red meat (P = 0.72 and 0.74), unprocessed red meat (P = 0.74 and 0.73), processed red meat (P = 0.72 and 0.15), and poultry intake (P = 0.67 for ractopamine). Our data suggest that the amount of meat-related exposure of β-agonists was low.
Keywords: cancer; meat consumption; ractopamine; urine; zilpaterol; β2-adrenergic agonists.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service. United States National Residue Program for Meat, Poultry, and Egg Products. 2013 Residue Sample Results. 2015
-
- USDA Food Safety and Inspection Service. United States National Residue Program for Meat, Poultry, and Egg Products. 2014 Residue Sample Results. 2015
-
- Baynes RE, Dedonder K, Kissell L, Mzyk D, Marmulak T, Smith G, et al. Health concerns and management of select veterinary drug residues. Food Chem Toxicol. 2016;88:112–22. - PubMed
-
- Mason S. Tissue residues and withdrawal times. In: Riviere JE, editor. Comparative Pharmacokinetics, Principles, Techniques & Applications. 2. West Sussex, UK: Wiley Blackwell; 2011. pp. 413–23.
-
- Kuiper HA, Noordam MY, van Dooren-Flipsen MM, Schilt R, Roos AH. Illegal use of beta-adrenergic agonists: European Community. J Anim Sci. 1998;76:195–207. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

