Expression, purification, and analysis of three recombinant ECD disintegrins (r-colombistatins) from P-III class snake venom metalloproteinases affecting platelet aggregation and SK-MEL-28 cell adhesion
- PMID: 27641750
- PMCID: PMC5175399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.09.007
Expression, purification, and analysis of three recombinant ECD disintegrins (r-colombistatins) from P-III class snake venom metalloproteinases affecting platelet aggregation and SK-MEL-28 cell adhesion
Abstract
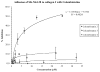
Crotalid venoms are rich sources of components that affect the hemostatic system. Snake venom metalloproteinases are zinc-dependent enzymes responsible for hemorrhage that also interfere with hemostasis. The disintegrin domain is a part of snake venom metalloproteinases, which involves the binding of integrin receptors. Integrins play an essential role in cancer survival and invasion, and they have been major targets for drug development and design. Both native and recombinant disintegrins have been widely investigated for their anti-cancer activities in biological systems as well as in vitro and in vivo systems. Here, three new cDNAs encoding ECD disintegrin-like domains of metalloproteinase precursor sequences obtained from a Venezuelan mapanare (Bothrops colombiensis) venom gland cDNA library have been cloned. Three different N- and C-terminal truncated ECD disintegrin-like domains of metalloproteinases named colombistatins 2, 3, and 4 were amplified by PCR, cloned into a pGEX-4T-1 vector, expressed in Escherichia coli BL21, and tested for inhibition of platelet aggregation and inhibition of adhesion of human skin melanoma (SK-Mel-28) cancer cell lines on collagen I. Purified recombinant colombistatins 2, 3, and 4 were able to inhibit ristocetin- and collagen-induced platelet aggregation. r-Colombistatins 2 showed the most potent inhibiting SK-Mel-28 cancer cells adhesion to collagen. These results suggest that colombistatins may have utility in the development of therapeutic tools in the treatment of melanoma cancers and also thrombotic diseases.
Keywords: Bothrops colombiensis; Colombistatins; ECD disintegrin-like domain; SK-Mel-28; Tumor.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Albelda SM, Mette SA, Elder DE, Stewart R, Damjanovich L, Herlyn M, Buck CA. Integrin distribution in malignant melanoma: association of the j93 subunit with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6757–6764. - PubMed
-
- . Principles of Laboratory Animal Care. National Institute of Health; USA: 1985. Pub, 85 No. 23.
-
- Bjarnason JB, Fox JW. Hemorrhagic metalloproteinases from snake venom. Pharmacol Ther. 1994;62:325–372. - PubMed
-
- Boukerche HO, Berthier-Vergnes M, Bailly JF, Dore LK, Leung JL, McGregor A monoclonal antibody (LYP18) directed against the blood platelet glycoprotein Ib/IIIa complex inhibits human melanoma growth in vivo. Blood. 1989;74:909–912. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

