Persistent Homology Analysis of Brain Artery Trees
- PMID: 27642379
- PMCID: PMC5026243
- DOI: 10.1214/15-AOAS886
Persistent Homology Analysis of Brain Artery Trees
Abstract
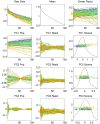
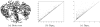
New representations of tree-structured data objects, using ideas from topological data analysis, enable improved statistical analyses of a population of brain artery trees. A number of representations of each data tree arise from persistence diagrams that quantify branching and looping of vessels at multiple scales. Novel approaches to the statistical analysis, through various summaries of the persistence diagrams, lead to heightened correlations with covariates such as age and sex, relative to earlier analyses of this data set. The correlation with age continues to be significant even after controlling for correlations from earlier significant summaries.
Keywords: Persistent homology; angiography; statistics; topological data analysis; tree-structured data.
Figures


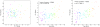






References
-
- Adcock A, Carlsson E, Carlsson G. The ring of algebraic functions on persistence bar codes. 2013 2013. Available at arXiv:1304.0530.
-
- Aydin B, Pataki G, Wang H, Bullitt E, Marron JS. A principal component analysis for trees. Ann Appl Stat. 2009;3:1597–1615. MR2752149.
-
- Aylward S, Bullitt E. Initialization, noise, singularities, and scale in height ridge traversal for tubular object centerline extraction. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2002;21:61–75. - PubMed
-
- Barden D, Le H, Owen M. Central limit theorems for Fréchet means in the space of phylogenetic trees. Electron J Probab. 2013;18(25):25. MR3035753.
-
- Barden D, Le H, Owen M. Limiting behaviour of Fréchet means in the space of phylogenetic trees. 2014 Preprint. Available at arXiv:1409.7602v1.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
