Optical Coherence Tomography of Retinal Degeneration in Royal College of Surgeons Rats and Its Correlation with Morphology and Electroretinography
- PMID: 27644042
- PMCID: PMC5028068
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162835
Optical Coherence Tomography of Retinal Degeneration in Royal College of Surgeons Rats and Its Correlation with Morphology and Electroretinography
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the correlation between optical coherence tomography (OCT) and the histological, ultrastructural and electroretinography (ERG) findings of retinal degeneration in Royal College of Surgeons (RCS-/-) rats.
Materials and methods: Using OCT, we qualitatively and quantitatively observed the continual retinal degeneration in RCS-/- rats, from postnatal (PN) day 17 until PN day 111. These findings were compared with the corresponding histological, electron microscopic, and ERG findings. We also compared them to OCT findings in wild type RCS+/+ rats, which were used as controls.
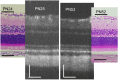
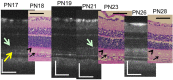
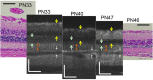
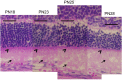
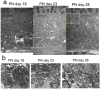
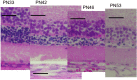
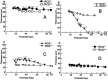
Results: After PN day 17, the hyperreflective band at the apical side of the photoreceptor layer became blurred. The inner segment (IS) ellipsoid zone then became obscured, and the photoreceptor IS and outer segment (OS) layers became diffusely hyperreflective after PN day 21. These changes correlated with histological and electron microscopic findings showing extracellular lamellar material that accumulated in the photoreceptor OS layer. After PN day 26, the outer nuclear layer became significantly thinner (P < 0.01) and hyperreflective compared with that in the controls; conversely, the photoreceptor IS and OS layers, as well as the inner retinal layers, became significantly thicker (P < 0.001 and P = 0.05, respectively). The apical hyperreflective band, as well as the IS ellipsoid zone, gradually disappeared between PN day 20 and PN day 30; concurrently, the ERG a- and b-wave amplitudes deteriorated. In contrast, the thicknesses of the combined retinal pigment epithelium and choroid did not differ significantly between RCS-/- and RCS+/+ rats.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that OCT demonstrates histologically validated photoreceptor degeneration in RCS rats, and that OCT findings partly correlate with ERG findings. We propose that OCT is a less invasive and useful method for evaluating photoreceptor degeneration in animal models of retinitis pigmentosa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Gal A, Li Y, Thompson DA, Weir j, Orth U, Jacobson SG, et al. Mutations in MERTK, the human orthologue of the RCS rat retinal dystrophy gene, cause retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Genet. 2000;26:270–271. - PubMed
-
- D’Cruz PM, Yasumura D, Weir J, Matthes MT, Abderrahim H, LaVail MM, et al. Mutation of the receptor tyrosine kinase gene MERTK in the retinal dystrophic RCS rat. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:645–651. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

