Mutation of the 3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 (PDK1) Substrate-Docking Site in the Developing Brain Causes Microcephaly with Abnormal Brain Morphogenesis Independently of Akt, Leading to Impaired Cognition and Disruptive Behaviors
- PMID: 27644329
- PMCID: PMC5108884
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00230-16
Mutation of the 3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 (PDK1) Substrate-Docking Site in the Developing Brain Causes Microcephaly with Abnormal Brain Morphogenesis Independently of Akt, Leading to Impaired Cognition and Disruptive Behaviors
Abstract
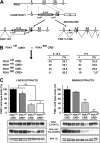
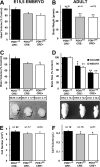
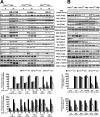
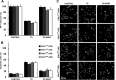
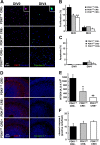
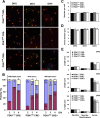
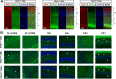
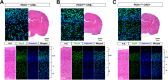
The phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway plays essential roles during neuronal development. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) coordinates the PI 3-kinase signals by activating 23 kinases of the AGC family, including Akt. Phosphorylation of a conserved docking site in the substrate is a requisite for PDK1 to recognize, phosphorylate, and activate most of these kinases, with the exception of Akt. We exploited this differential mechanism of regulation by generating neuron-specific conditional knock-in mice expressing a mutant form of PDK1, L155E, in which the substrate-docking site binding motif, termed the PIF pocket, was disrupted. As a consequence, activation of all the PDK1 substrates tested except Akt was abolished. The mice exhibited microcephaly, altered cortical layering, and reduced circuitry, leading to cognitive deficits and exacerbated disruptive behavior combined with diminished motivation. The abnormal patterning of the adult brain arises from the reduced ability of the embryonic neurons to polarize and extend their axons, highlighting the essential roles that the PDK1 signaling beyond Akt plays in mediating the neuronal responses that regulate brain development.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
