Stakeholders' perceptions of 10years of the Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines (GAP) - Results from a survey
- PMID: 27646029
- PMCID: PMC5357767
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.08.040
Stakeholders' perceptions of 10years of the Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines (GAP) - Results from a survey
Abstract
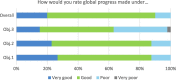
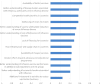
Ten years after the launch of the Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines (GAP), the World Health Organization (WHO) surveyed stakeholders to understand their perceptions of what the programme had achieved. This article provides a summary of the findings; the full report will be available on-line on the GAP website in November 2016 (http://www.who.int/influenza_vaccines_plan/en/). Seventy-seven responses were received from stakeholders including medical doctors, national influenza center officials, country immunization programme teams, surveillance and disease centers, policy-makers, researchers, vaccine manufacturers, and non-governmental organizations from 28 countries, representing all six WHO regions. Respondents cited GAP's biggest successes as capacity building in developing countries; raising international awareness of global needs in the event of a pandemic; and collaborative alignment of influenza stakeholders. The most commonly reported challenges were the limited progress in development of a broadly protective or universal vaccine and the perceived absence of a major increase in seasonal demand. These findings aligned with the perception that less global progress had been made under the third GAP objective, focused on research and development of better vaccines, than on increasing seasonal vaccine use (objective 1) and pandemic vaccine production capacity (objective 2). Respondents explained what they saw as the major challenges to development of better vaccines, including to development of a universal influenza vaccine. The majority of respondents agreed that the goal chosen at the GAP II consultation is still relevant. Results highlighted the importance of promoting research and development of better vaccines, both for facilitating uptake of seasonal vaccines and for ensuring timely vaccine availability in the event of a pandemic. As the GAP concludes its mandate this year, these findings will contribute to discussions on the impact of programme closure and how to address the key issues facing influenza stakeholders thereafter.
Keywords: Influenza vaccine; Pandemic preparedness; Seasonal influenza; Survey.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The 2015 global production capacity of seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccine.Vaccine. 2016 Oct 26;34(45):5410-5413. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.08.019. Epub 2016 Aug 13. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27531411 Free PMC article.
-
A global pandemic influenza vaccine action plan.Vaccine. 2006 Sep 29;24(40-41):6367-70. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.07.021. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 17240560
-
A decade of adaptation: Regulatory contributions of the World Health Organization to the Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines (2006-2016).Vaccine. 2016 Oct 26;34(45):5414-5419. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.07.025. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27498212
-
WHO initiative to increase global and equitable access to influenza vaccine in the event of a pandemic: supporting developing country production capacity through technology transfer.Vaccine. 2011 Jul 1;29 Suppl 1:A2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.02.079. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21684422 Review.
-
United States of America Department of Health and Human Services support for advancing influenza vaccine manufacturing in the developing world.Vaccine. 2011 Jul 1;29 Suppl 1:A48-50. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.02.080. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21684430 Review.
Cited by
-
Report on the second WHO integrated meeting on development and clinical trials of influenza vaccines that induce broadly protective and long-lasting immune responses: Geneva, Switzerland, 5-7 May 2014.Vaccine. 2015 Nov 27;33(48):6503-10. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26478203 Free PMC article.
-
Building the global vaccine manufacturing capacity needed to respond to pandemics.Vaccine. 2021 Mar 19;39(12):1667-1669. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.02.017. Epub 2021 Feb 24. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 33640143 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Postpandemic Sentinel Surveillance of Respiratory Diseases in the Context of the World Health Organization Mosaic Framework: Protocol for a Development and Evaluation Study Involving the English Primary Care Network 2023-2024.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Apr 3;10:e52047. doi: 10.2196/52047. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 38569175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global pandemic influenza action plan to increase vaccine supply. 2006. <http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/69388/1/WHO_IVB_06.13_eng.pdf> [accessed 18.05.16]
-
- World Health Organization Report of the second WHO Consultation on the Global Action Plan for Influenza Vaccines (GAP) 2011. <http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44794/1/9789241564410_eng.pdf> [accessed 18.05.16]
-
- World Health Organization GAP progress materials. 2016. <http://www.who.int/influenza_vaccines_plan/resources/progress_materials... [accessed 27.06.16]
-
- Available at the following web-link: <http://www.who.int/phi/links/GAP_survey_questionnaire2016.pdf?ua=1>.
-
- Participants lists available at: <http://www.who.int/influenza_vaccines_plan/news/gap_lop.pdf?ua=1>.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

