Prefrontal connections express individual differences in intrinsic resistance to trading off honesty values against economic benefits
- PMID: 27646044
- PMCID: PMC5028845
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33263
Prefrontal connections express individual differences in intrinsic resistance to trading off honesty values against economic benefits
Abstract
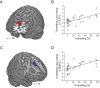
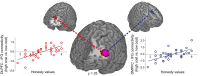
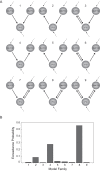
Individuals differ profoundly when they decide whether to tell the truth or to be dishonest, particularly in situations where moral motives clash with economic motives, i.e., when truthfulness comes at a monetary cost. These differences should be expressed in the decision network, particularly in prefrontal cortex. However, the interactions between the core players of the decision network during honesty-related decisions involving trade-offs with economic costs remain poorly understood. To investigate brain connectivity patterns associated with individual differences in responding to economic costs of truthfulness, we used functional magnetic resonance imaging and measured brain activations, while participants made decisions concerning honesty. We found that in participants who valued honesty highly, dorsolateral and dorsomedial parts of prefrontal cortex were more tightly coupled with the inferior frontal cortex when economic costs were high compared to when they were low. Finer-grained analysis revealed that information flow from the inferior frontal cortex to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and bidirectional information flow between the inferior frontal cortex and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex was associated with a reduced tendency to trade off honesty for economic benefits. Our findings provide a novel account of the neural circuitry that underlies honest decisions in the face of economic temptations.
Figures

References
-
- Healy P. M. & Wahlen J. M. A review of the earnings management literature and its implications for standard setting. Accounting Horizons 13, 365–383 (1999).
-
- Gibson R., Tanner C. & Wagner A. Preferences for truthfulness: Heterogeneity among and within individuals. Am. Econ. Rev. 103, 532–548 (2013).
-
- Abe N. How the brain shapes deception: An integrated review of the literature. Neuroscientist 17, 560–574 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner T., Fischbacher U., Feierabend A., Lutz K. & Fehr E. The neural circuitry of a broken promise. Neuron 64, 756–770 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

